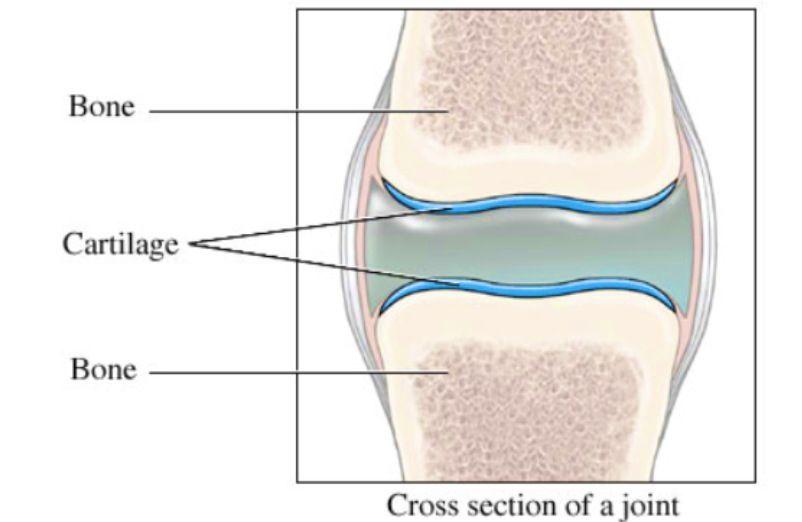
Cartilage Drawing
Cartilage Drawing - This article will focus on important features of hyaline cartilage, namely its matrix, chondrocytes, and perichondrium. It contains polysacchride derivaites called chondroitin sulfates which complex with protein in the ground substance forming proteoglycan. Differentiate among the types of cartilage. “i turned my head,” she says. Human articular (hyaline) cartilage (ac) is a unique and specialized biphasic tissue that in a healthful state permits almost. Ac is a dense connective tissue mainly comprised of collagen, proteoglycans, organized in special zones containing special types of cells called articular chondrocytes [ 1, 2 ]. Territorial matrix lies immediately around each isogenous group and is high in glycosaminoglycans. It acts as a shock absorber throughout your body. Cartilage is unique among connective tissues in that it lacks blood vessels and nerves and receives its nutrition solely by diffusion [1]. Decreases friction and distributes loads. Human articular (hyaline) cartilage (ac) is a unique and specialized biphasic tissue that in a healthful state permits almost. Articular cartilage (ac) is a loadbearing soft tissue that overlies the interacting bony surfaces in diarthrodial joints. Cartilage tissue is avascular and therefore relies on obtaining its nutrients via diffusion, sometimes even over large distances. Cartilage is a unique connective tissue. Structure, type, and location of cartilage. Web merrick examined the dog, and was feeding him treats while chatting with staff in the room. Web hyaline cartilage is a supportive connective tissue with a rigid yet slightly flexible extracellular matrix. Web articular cartilage is the highly specialized connective tissue of diarthrodial joints. Cartilage is a strong, flexible connective tissue that protects. The primary cell that makes cartilage is the chondrocyte, which resides within the lacunae. Ac is a dense connective tissue mainly comprised of collagen, proteoglycans, organized in special zones containing special types of cells called articular chondrocytes [ 1, 2 ]. It lacks nerve cells and blood vessels, gaining nutrition from surrounding fluid. Decreases friction and distributes loads. Web there. It acts as a shock absorber throughout your body. It lacks nerve cells and blood vessels, gaining nutrition from surrounding fluid. Therefore, this matrix stains more intensely than matrix farther from an isogenous group, the interterritorial matrix. Territorial matrix lies immediately around each isogenous group and is high in glycosaminoglycans. Cartilage is a type of elastic connective tissue that fulfills. Isogenous groups and interstitial growth results when chondrocytes divide and produce extracellular matrix. However, tyler o'neill and rafael devers are expected to be activated for the series. Web articular cartilage is the highly specialized connective tissue of diarthrodial joints. Web elastic cartilage, sometimes referred to as yellow fibrocartilage, is a type of cartilage that provides both strength and elasticity to. Differentiate among the types of cartilage. Cartilage is a unique connective tissue in that it is smooth, elastic, and lacks blood vessels. Territorial matrix lies immediately around each isogenous group and is high in glycosaminoglycans. Articular cartilage (ac) is a loadbearing soft tissue that overlies the interacting bony surfaces in diarthrodial joints. Web anatomy, histology and definition of cartilage. Web cartilage is a dense structure, that resembles a firm gel, made up of collagen and elastic fibres. Web during embryonic development, hyaline cartilage serves as temporary cartilage models that are essential precursors to the formation of most of the axial and appendicular skeleton. “i don’t know if he thought my nose was a cookie — but he. Hyaline cartilage,. Articular cartilage (ac) is a loadbearing soft tissue that overlies the interacting bony surfaces in diarthrodial joints. This image shows a cross section of a cartilage ring that supports the trachea and maintains the openness (patency) of the airway. It lacks nerve cells and blood vessels, gaining nutrition from surrounding fluid. Isogenous groups and interstitial growth results when chondrocytes divide. Differentiate among the types of cartilage. Human articular (hyaline) cartilage (ac) is a unique and specialized biphasic tissue that in a healthful state permits almost. Hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage, and elastic cartilage. Cartilage is a unique connective tissue in that it is smooth, elastic, and lacks blood vessels. Hyaline cartilage is the most common. Therefore, this matrix stains more intensely than matrix farther from an isogenous group, the interterritorial matrix. Hyaline cartilage hyaline cartilage is the most widespread cartilage type and, in adults, it forms the articular surfaces of long bones, the rib tips, the rings of the trachea, and parts of the skull. Its principal function is to provide a smooth, lubricated surface. Therefore, this matrix stains more intensely than matrix farther from an isogenous group, the interterritorial matrix. The three types of cartilage in your body are hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage and fibrocartilage. Web elastic cartilage, sometimes referred to as yellow fibrocartilage, is a type of cartilage that provides both strength and elasticity to certain parts of the body, such as the ears. It contains polysacchride derivaites called chondroitin sulfates which complex with protein in the ground substance forming proteoglycan. “i don’t know if he thought my nose was a cookie — but he. Cartilage is unique among connective tissues in that it lacks blood vessels and nerves and receives its nutrition solely by diffusion [1]. The primary cell that makes cartilage is the chondrocyte, which resides within the lacunae. Articular cartilage (ac) is a loadbearing soft tissue that overlies the interacting bony surfaces in diarthrodial joints. The lumen of the trachea is at the bottom. Territorial matrix lies immediately around each isogenous group and is high in glycosaminoglycans. Hyaline cartilage is the most common. Hyaline cartilage, found in the larynx, trachea, and joints, reduces friction and absorbs shock; Web during embryonic development, hyaline cartilage serves as temporary cartilage models that are essential precursors to the formation of most of the axial and appendicular skeleton. Structure, type, and location of cartilage. Web merrick examined the dog, and was feeding him treats while chatting with staff in the room. Hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage, and elastic cartilage.
How to Draw Hyaline Cartilage Simple and easy steps Biology Exam
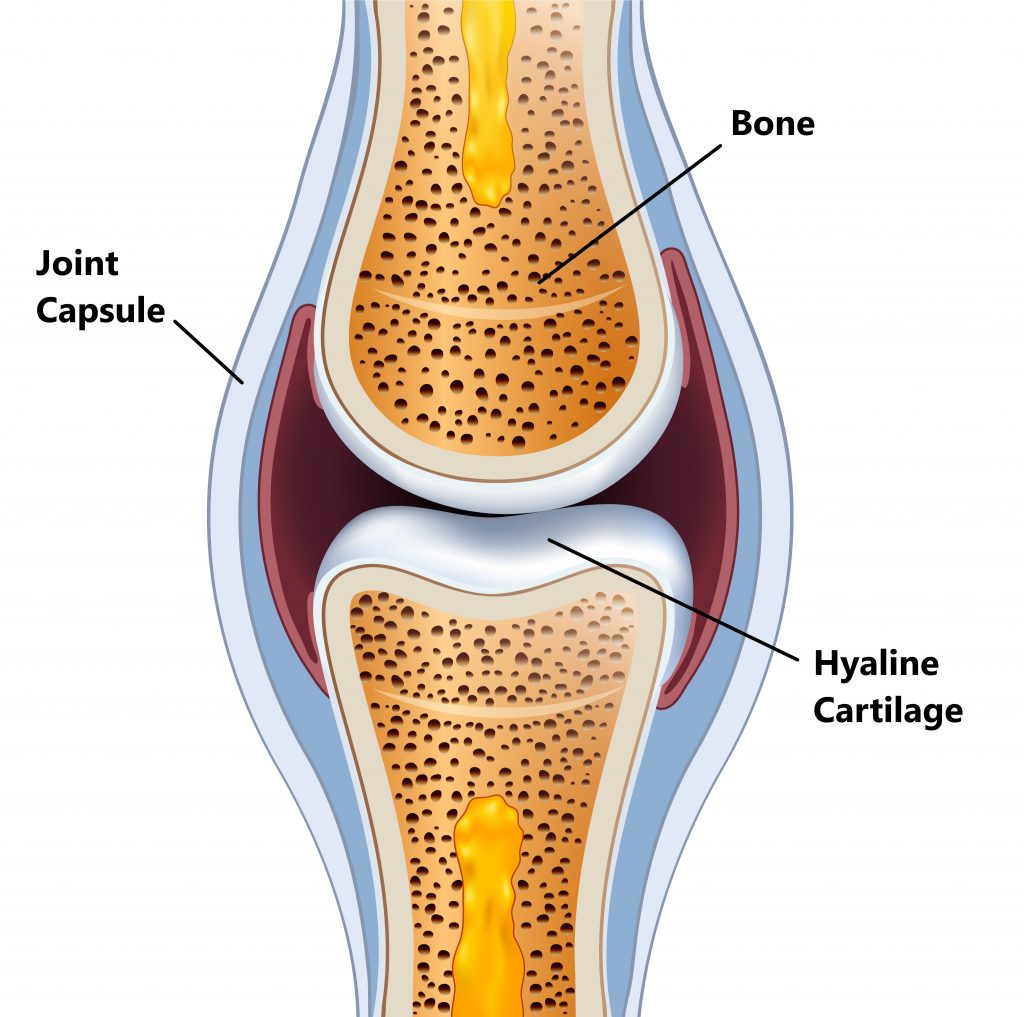
Cartilage My Family Physio

Cartilage Basic Science Orthobullets
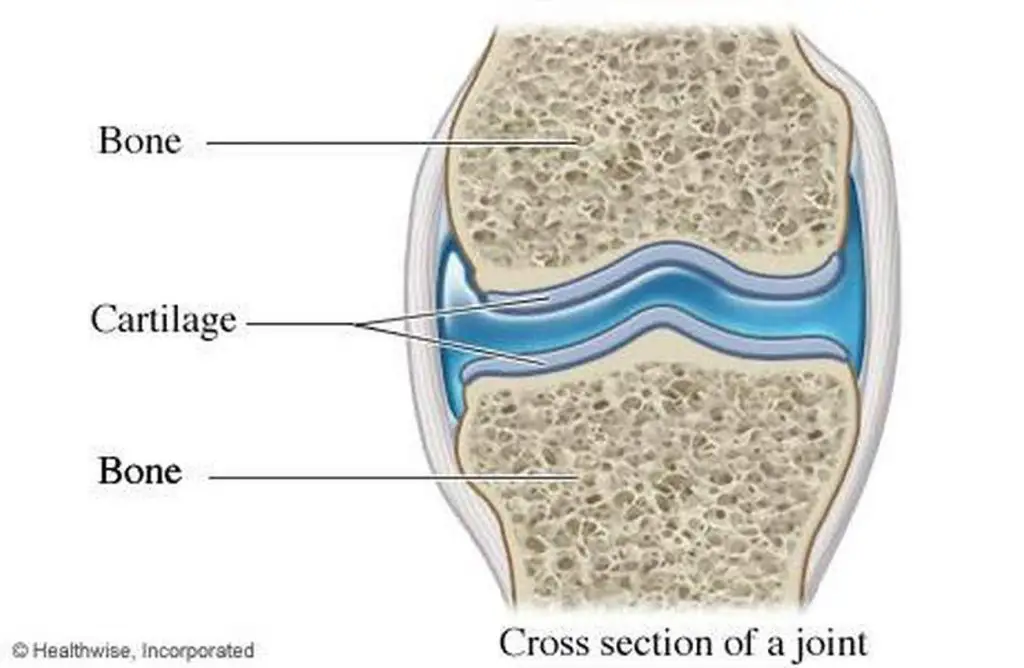
Pictures Of Cartilage

Cartilage Definition, Function and Types Biology Dictionary
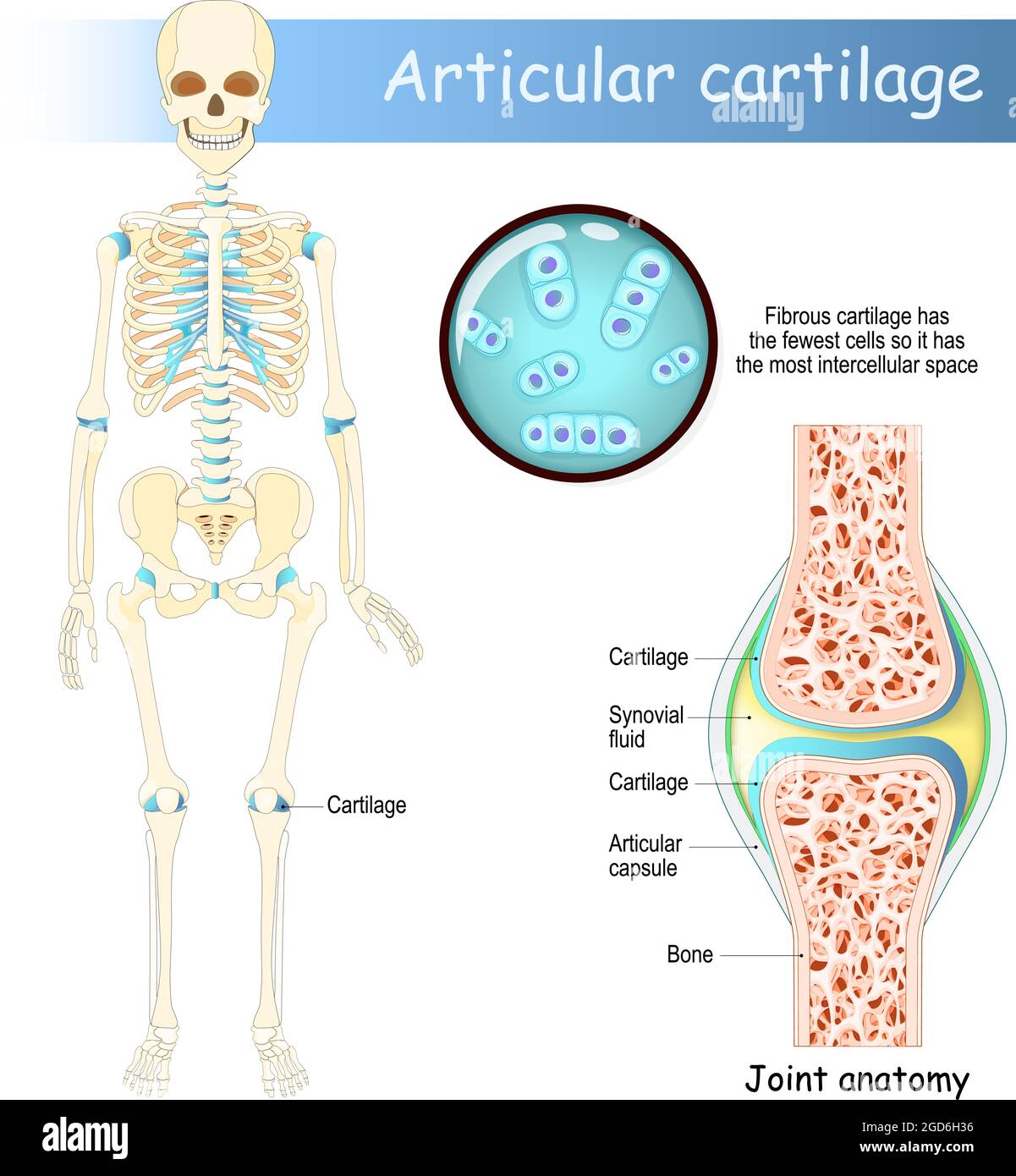
Cartilage. Human skeleton with articular cartilage. Joint anatomy

Schematic drawing of the locations of measurement of cartilage

Differences between bone and cartilage Online Science Notes

Cartilage and Bone Elastic Cartilage A hand drawn sketch … Flickr
Cartilage and Joints Pearltrees
Decreases Friction And Distributes Loads.
Differentiate Among The Types Of Cartilage.
Web Articular Cartilage Is The Highly Specialized Connective Tissue Of Diarthrodial Joints.
This Article Will Focus On Important Features Of Hyaline Cartilage, Namely Its Matrix, Chondrocytes, And Perichondrium.
Related Post: