Cranial Drawer Test Dog
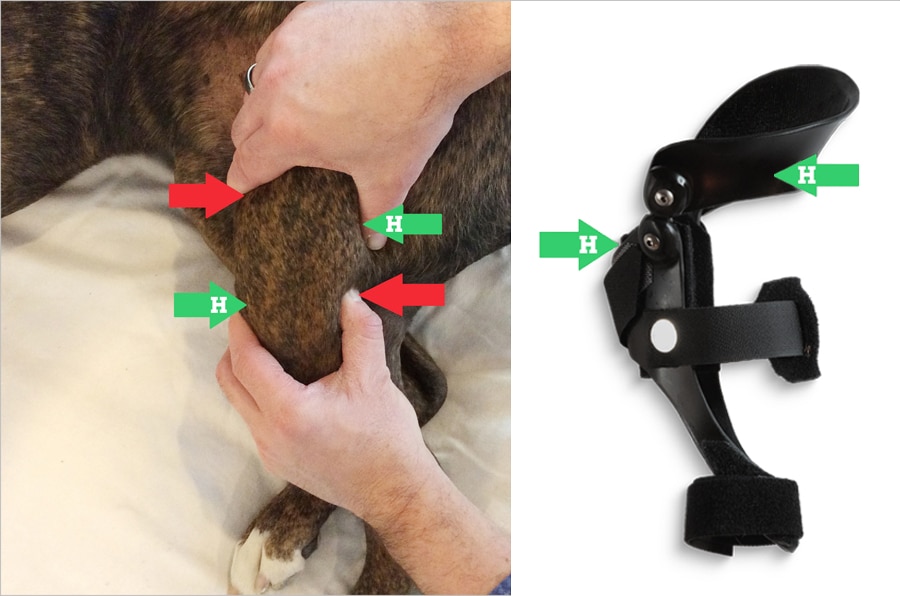
Cranial Drawer Test Dog - 6 evaluation of cd signs and ctt, which are diagnostic tests for ccld, should be performed during examination. (see figure 1 & cranial drawer & cranial tibial thrust tests.) Web a positive tibial compression test and cranial drawer test confirm cclr. Immature dogs are often misdiagnosed with crclr because they have greater than expected cranial drawer sign due to normal puppy laxity. Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to confirm a problem with the ccl are the “cranial drawer test” and the “tibial thrust test.” these tests confirm abnormal motion in the knee and hence a rupture of the ccl. In general, radiographic images are used to visualize the instability of the stifle joint by tibial compression, to detect effusion and secondary osteoarthritic changes. In this test, the dog’s knee is slightly bent and anterior pressure is applied to the distal femur while posterior pressure is applied to the proximal tibia. Web pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. Web welcome to our canine physiotherapy tutorial video, where we will guide you through two essential diagnostic tests for evaluating cranial cruciate ligament (. The cranial drawer assessment is best done on the laterally recumbent animal. (see figure 1 & cranial drawer & cranial tibial thrust tests.) In this test, the dog’s knee is slightly bent and anterior pressure is applied to the distal femur while posterior pressure is applied to the proximal tibia. Some dogs are more relaxed in the standing position than when restrained in lateral recumbency. Web diagnosis of cranial cruciate ligament rupture. Web definitive diagnosis of rupture of the ccl demands an assessment of stifle joint stability by means of the cranial “drawer” test, the tibial compression test, or both tests. Web a positive tibial compression test and cranial drawer test confirm cclr. Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to confirm a problem with the ccl are the “cranial drawer test”. In this test, the dog’s knee is slightly bent and anterior pressure is applied to the distal femur while posterior pressure is applied to the proximal tibia. Some dogs are more relaxed in the standing position than when restrained in lateral recumbency. Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to confirm a problem with the ccl are the “cranial drawer. Web welcome to our canine physiotherapy tutorial video, where we will guide you through two essential diagnostic tests for evaluating cranial cruciate ligament (. Immature dogs are often misdiagnosed with crclr because they have greater than expected cranial drawer sign due to normal puppy laxity. Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to confirm a problem with the ccl are. Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to confirm a problem with the ccl are the “cranial drawer test” and the “tibial thrust test.” these tests confirm abnormal motion in the knee and hence a rupture of the ccl. Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to assess the crcl include the ‘cranial drawer test’ and the ‘tibial compression test.’. Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to confirm a problem with the ccl are the “cranial drawer test” and the “tibial thrust test.” these tests confirm abnormal motion in the knee and hence a rupture of the ccl. In general, radiographic images are used to visualize the instability of the stifle joint by tibial compression, to detect effusion and. Sliding of the distal femur over the proximal tibia Web definitive diagnosis of rupture of the ccl demands an assessment of stifle joint stability by means of the cranial “drawer” test, the tibial compression test, or both tests. Web to test for cranial tibial translation, perform the cranial drawer test (figure 6). Web pain upon forced full extension of the. Web diagnosis of cranial cruciate ligament rupture is usually made by a positive cranial drawer sign. 6 evaluation of cd signs and ctt, which are diagnostic tests for ccld, should be performed during examination. Sliding of the distal femur over the proximal tibia (see figure 1 & cranial drawer & cranial tibial thrust tests.) Web the correct performance of either. Web welcome to our canine physiotherapy tutorial video, where we will guide you through two essential diagnostic tests for evaluating cranial cruciate ligament (. The examiner stands behind the dog and places a thumb on the caudal aspect of the femoral. Web a positive tibial compression test and cranial drawer test confirm cclr. Web definitive diagnosis of rupture of the. The examiner stands behind the dog and places a thumb on the caudal aspect of the femoral. In a mature dog, a healthy, intact cranial cruciate ligament will not permit cranial tibial translation with the stifle held in extension or in flexion.3 in an immature dog, puppy laxity may permit a few millimeters of cranial and caudal tibial translation, but.. Web a positive tibial compression test and cranial drawer test confirm cclr. Web diagnosis of cranial cruciate ligament rupture is usually made by a positive cranial drawer sign. Web to test for cranial tibial translation, perform the cranial drawer test (figure 6). Sliding of the distal femur over the proximal tibia The cranial drawer assessment is best done on the laterally recumbent animal. Web welcome to our canine physiotherapy tutorial video, where we will guide you through two essential diagnostic tests for evaluating cranial cruciate ligament (. Some dogs are more relaxed in the standing position than when restrained in lateral recumbency. In a mature dog, a healthy, intact cranial cruciate ligament will not permit cranial tibial translation with the stifle held in extension or in flexion.3 in an immature dog, puppy laxity may permit a few millimeters of cranial and caudal tibial translation, but. Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to confirm a problem with the ccl are the “cranial drawer test” and the “tibial thrust test.” these tests confirm abnormal motion in the knee and hence a rupture of the ccl. Web pain upon forced full extension of the stifle is a simple test that is suggestive of early crcld. 6 evaluation of cd signs and ctt, which are diagnostic tests for ccld, should be performed during examination. Web definitive diagnosis of rupture of the ccl demands an assessment of stifle joint stability by means of the cranial “drawer” test, the tibial compression test, or both tests. Web the correct performance of either test is a learned skill, mastered only after much experience and practice on healthy dogs as well as those with partial or complete crclrs. Web specific palpation techniques that veterinarians use to assess the crcl include the ‘cranial drawer test’ and the ‘tibial compression test.’ these tests can confirm abnormal motion within the knee consistent with rupture of the crcl. The cranial drawer test and tibial compression tests are important for assessing palpable instability. Immature dogs are often misdiagnosed with crclr because they have greater than expected cranial drawer sign due to normal puppy laxity.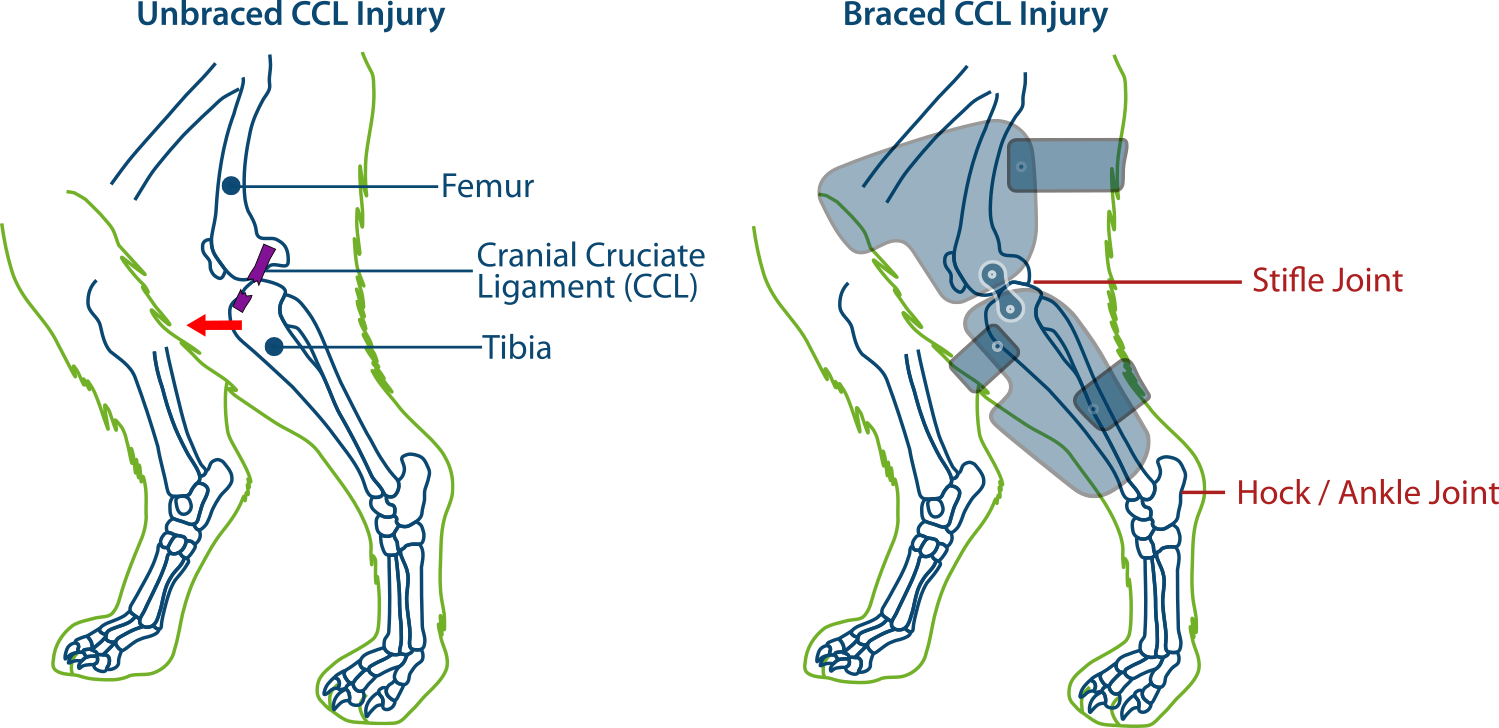
Cranial Cruciate Ligament (CCL) Tears in Dogs and Bracing — PawOpedic

Cranial Cruciate Ligament Disease in Dogs New England Veterinary Services
Surgery NOT An Option? Torn ACL Dog Knee Braces

Cruciate Disease The Cranial Drawer Test YouTube

Pathology, Diagnosis, and Treatment Goals of Cranial Cruciate Ligament

Cranial Nerve Testing Chart

Positive cranial drawer sign in a dog with a cranial (anterior

4 Tips To The Perfect Dog Brace Cast Hero Blog

Cranial Cruciate Ligament Medical Diagram Torn Knee Ligament in Dogs

Cranial drawer test/sign for diagnosis of cranial cruciate ligament
(See Figure 1 & Cranial Drawer & Cranial Tibial Thrust Tests.)
In General, Radiographic Images Are Used To Visualize The Instability Of The Stifle Joint By Tibial Compression, To Detect Effusion And Secondary Osteoarthritic Changes.
The Examiner Stands Behind The Dog And Places A Thumb On The Caudal Aspect Of The Femoral.
In This Test, The Dog’s Knee Is Slightly Bent And Anterior Pressure Is Applied To The Distal Femur While Posterior Pressure Is Applied To The Proximal Tibia.
Related Post: