Draw Atp Molecule
Draw Atp Molecule - A triphosphate chain consisting of three phosphate groups. Explain atp's role as the cellular energy currency. This molecule can be thought of as the primary energy currency of cells in much the same way that money is the currency that people exchange for things they. Atp captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes. Web by the end of this section, you will be able to do the following: Web adenosine triphosphate, or atp, is a small, relatively simple molecule. Web an atp molecule | learn science at scitable. This model shows the structure of atp, a molecule that provides energy for cellular processes, including protein phosphorylation. Every mole of atp that is hydrolysed releases 30.6kj when the bond is broken. Web nad + + 2 e − + 2 h + → nadh + h +. Every mole of atp that is hydrolysed releases 30.6kj when the bond is broken. Web 3d model of atp. Atp is a small, relatively simple molecule (figure \(\pageindex{1}\)), but within some of its bonds, it contains the potential for a quick burst of energy that can be harnessed to perform cellular work. Adenine, ribose, and three phosphate groups. Breaking of. Failed to load structure from its database. The bonds between the phosphates store available energy, which is released when they are broken by the addition of a water molecule (a procedure known as hydrolysis). Atp is a macromolecule known as a nucleic acid that is made of three main components or parts: Web an atp molecule | learn science at. Describe how energy releases through atp hydrolysis. Track the atoms in different colors if that helps. Atp has many important roles in the cell. Include what is and is not recycled. Learn more about the structure and function of atp in this article. Web atp is a small, relatively simple molecule (figure 6.13), but within some of its bonds, it contains the potential for a quick burst of energy that can be harnessed to perform cellular work. This molecule is composed of three parts: Also notable, atp stands for adenosine triphosphate. Fad + 2 e − + 2 h + → fadh 2.. Fad + 2 e − + 2 h + → fadh 2. Every mole of atp that is hydrolysed releases 30.6kj when the bond is broken. The energy released from the hydrolysis of atp into adp + p i is used to perform cellular work. A major role of atp is to bind to. Atp is a macromolecule known as. The three phosphate groups are labeled alpha, beta, and gamma from closest to furthest from the ribose sugar. This molecule is composed of three parts: This is a small, relatively simple molecule ( figure 6.13 ), but within some of its bonds, it contains the potential for a quick burst of. The energy released from the hydrolysis of atp into. Web atp structure and function. Web the atp molecule is hydrolsed into adenosine diphosphate (adp) and an inorganic phosphate ion with the release of chemical energy. The bonds between the phosphates store available energy, which is released when they are broken by the addition of a water molecule (a procedure known as hydrolysis). Atp consists of an adenosine base (blue),. Web atp structure and function. Web cells actually draw their energy from the phosphate tail of atp. Sweet foods provide a rich source of readily available glucose while other foods provide the materials needed to create glucose. Include what is and is not recycled. This model shows the structure of atp, a molecule that provides energy for cellular processes, including. The three phosphate groups are labeled alpha, beta, and gamma from closest to furthest from the ribose sugar. Sweet foods provide a rich source of readily available glucose while other foods provide the materials needed to create glucose. Like the other nucleotides amp is composed of a nitrogenous base (an adenine molecule) bonded to a ribose molecule and a single. Click on the structure to rotate it and view it. Every mole of atp that is hydrolysed releases 30.6kj when the bond is broken. This molecule can be thought of as the primary energy currency of cells in much the same way that money is the currency that people exchange for things they. This is a small, relatively simple molecule. This molecule can be thought of as the primary energy currency of cells in much the same way that money is the currency that people exchange for things they. Atp is a small, relatively simple molecule (figure \(\pageindex{1}\)), but within some of its bonds, it contains the potential for a quick burst of energy that can be harnessed to perform cellular work. A triphosphate chain consisting of three phosphate groups. Web atp is a small, relatively simple molecule (figure 6.13), but within some of its bonds, it contains the potential for a quick burst of energy that can be harnessed to perform cellular work. Atp captures chemical energy obtained from the breakdown of food molecules and releases it to fuel other cellular processes. Atp has many important roles in the cell. Web adenosine triphosphate, or atp, is a small, relatively simple molecule. Sweet foods provide a rich source of readily available glucose while other foods provide the materials needed to create glucose. The three phosphate groups are labeled alpha, beta, and gamma from closest to furthest from the ribose sugar. This molecule is composed of three parts: This model shows the structure of atp, a molecule that provides energy for cellular processes, including protein phosphorylation. Explain atp's role as the cellular energy currency. Web cells actually draw their energy from the phosphate tail of atp. Atp consists of an adenosine base (blue), a ribose sugar (pink) and a phosphate chain. Track the atoms in different colors if that helps. Web atp molecules are used by all living organism as energy to carry out life functions.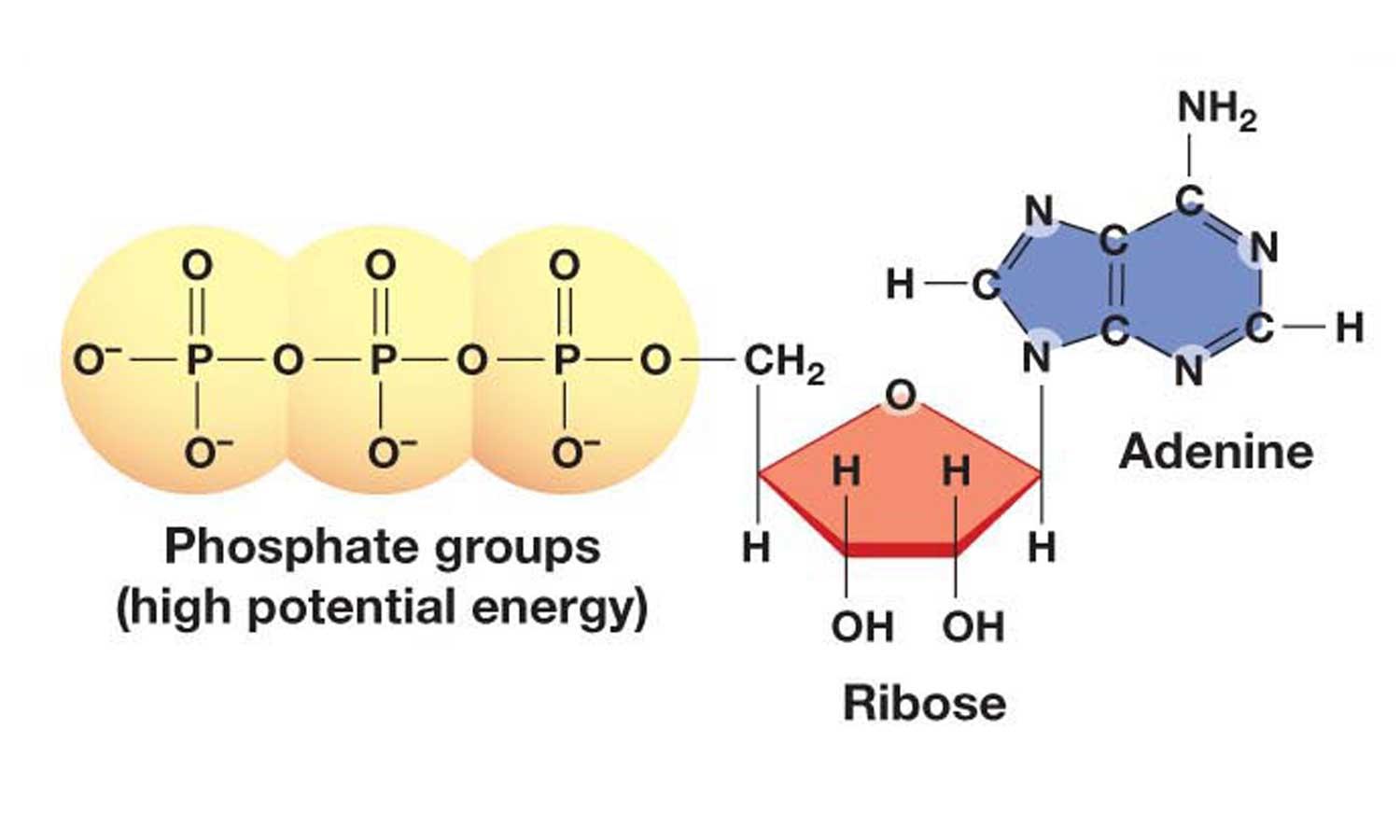
ATP and Sources of Energy.pptx on emaze
ATP Molecule
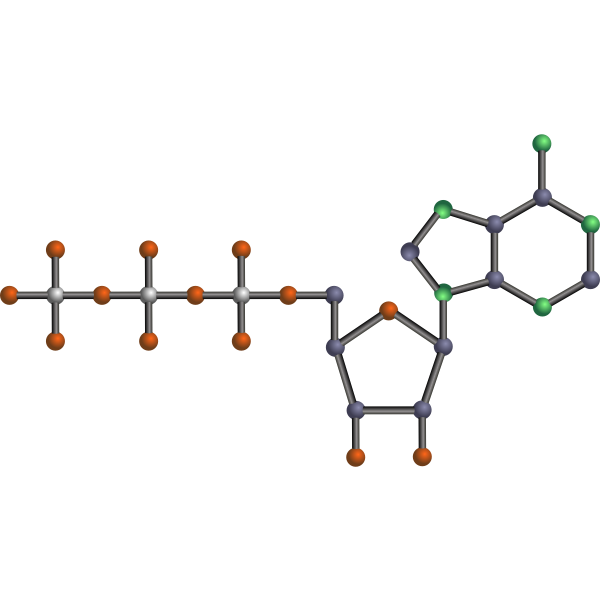
ATP molecule Free SVG

ATP définition et explications

ATP, molécule énergétique du vivant
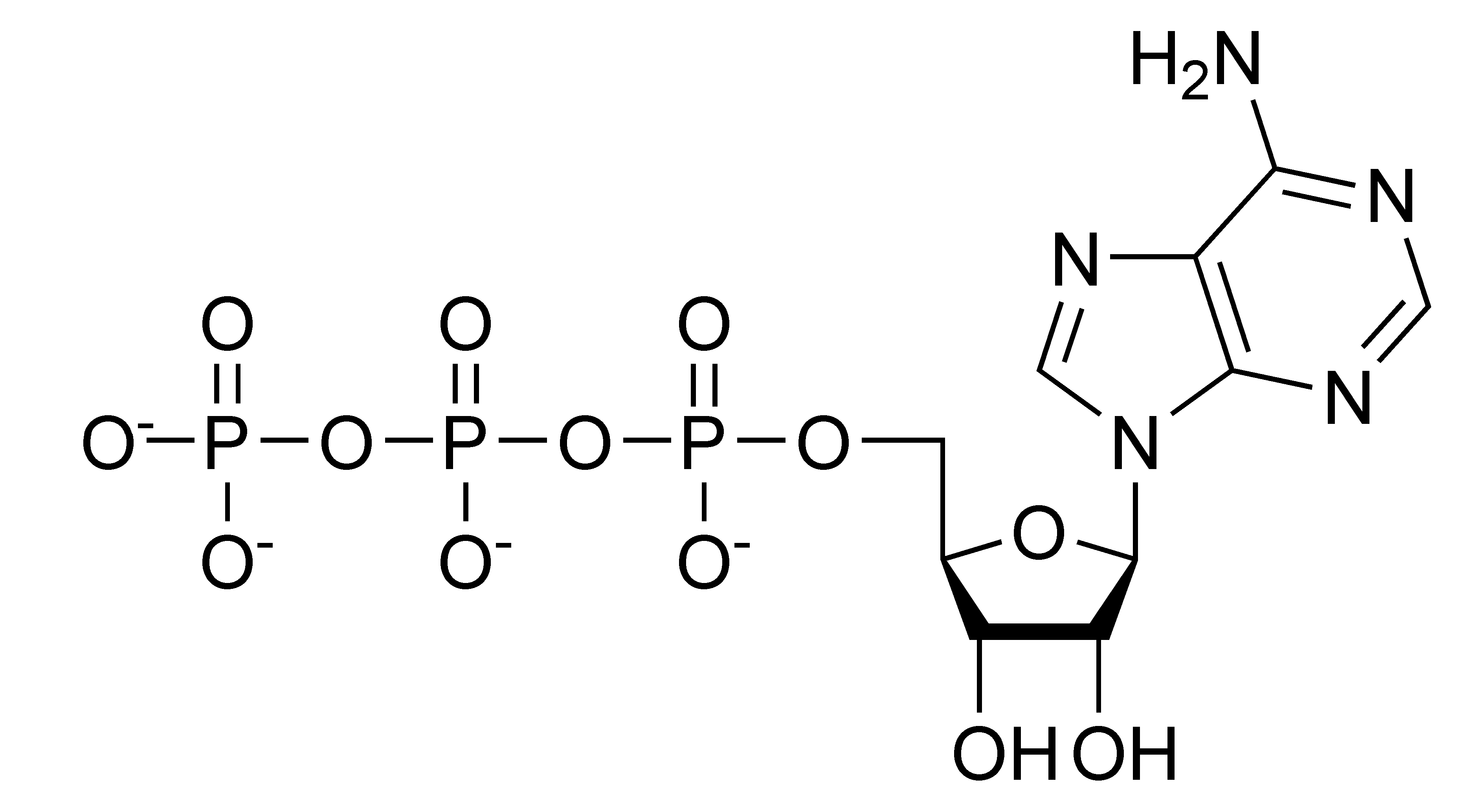
FileATP chemical structure.png Wikipedia
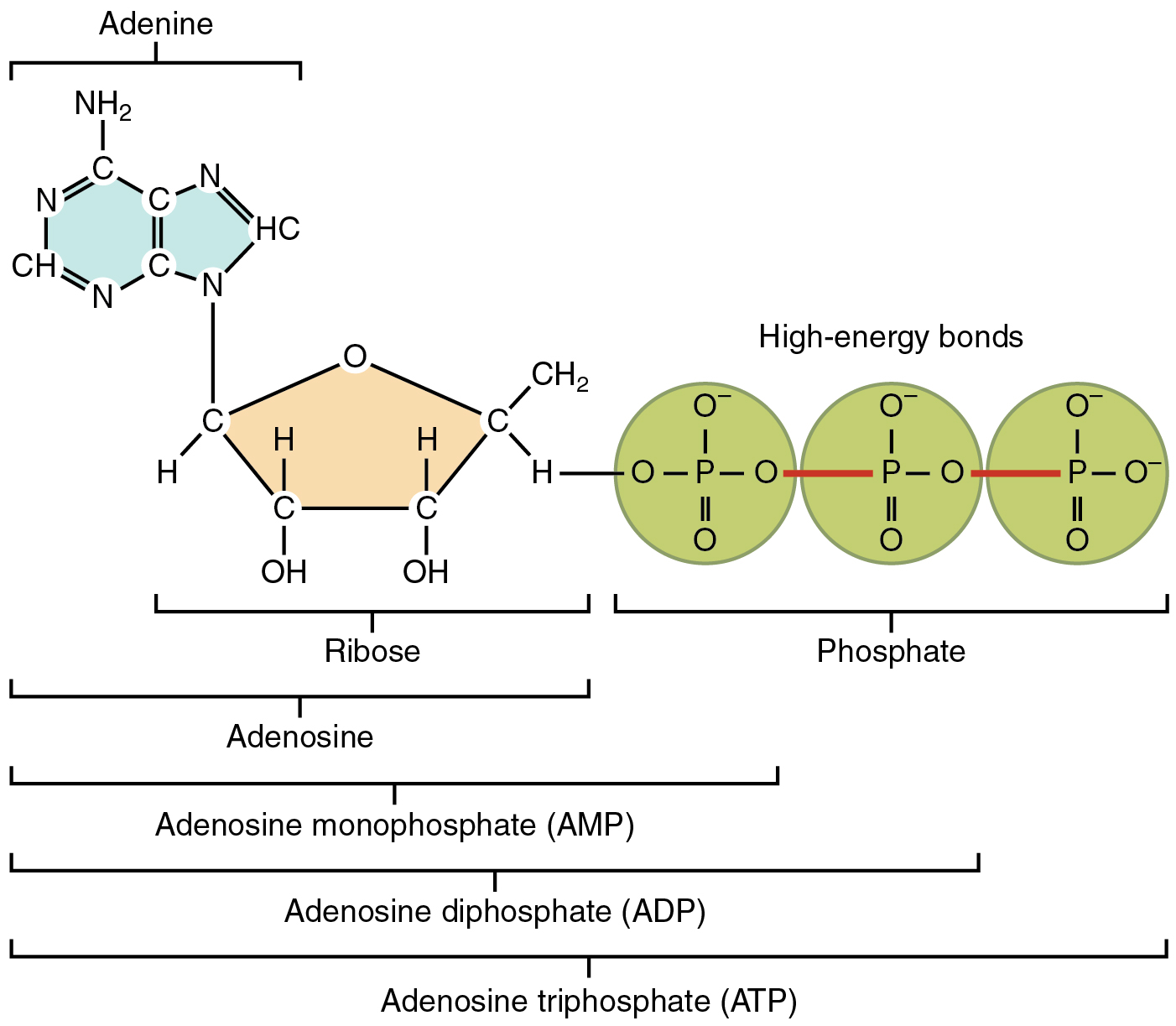
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Definition and Synthesis

What is Adenosine Triphosphate? Definition, Function & Structure

Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Definition and Synthesis
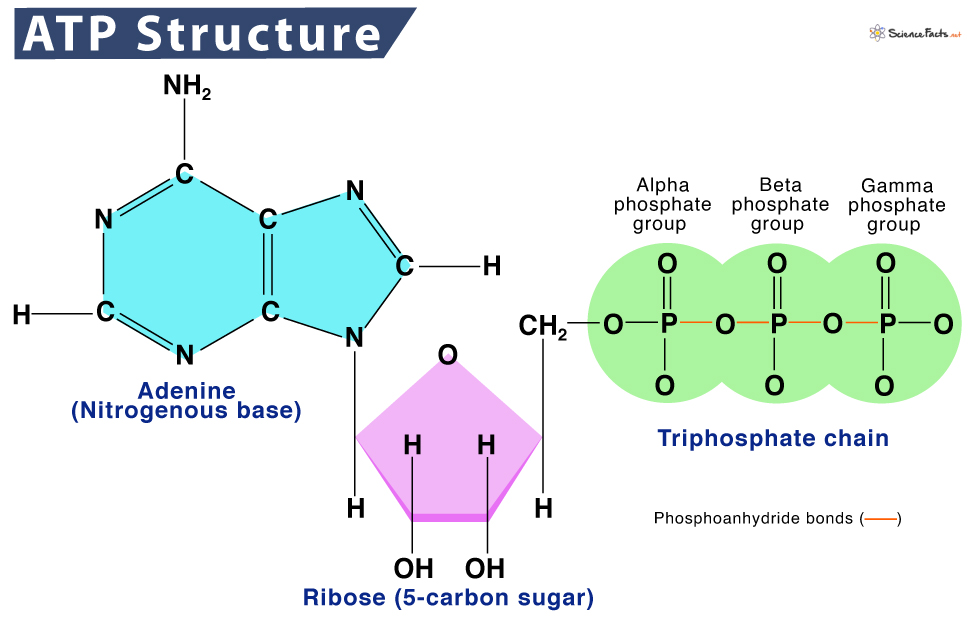
Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Definition, Structure, & Diagram
Every Mole Of Atp That Is Hydrolysed Releases 30.6Kj When The Bond Is Broken.
Like The Other Nucleotides Amp Is Composed Of A Nitrogenous Base (An Adenine Molecule) Bonded To A Ribose Molecule And A Single Phosphate Group.
Web 3D Model Of Atp.
It Is The Main Energy Currency Of The Cell, And It Is An End Product Of The Processes Of Photophosphorylation (Adding A Phosphate Group To A Molecule Using Energy From Light), Cellular Respiration, And Fermentation.
Related Post:
