Draw The Lewis Structure For A Carbon Monosulfide Molecule
Draw The Lewis Structure For A Carbon Monosulfide Molecule - The following procedure can be used to construct lewis electron structures for simple molecules. In carbon monosulfide, the oxidation state of the carbon. Before we can begin drawing the lewis structure for cos ( carbon monosulfide ), we need to determine. A compound with a molar mass of about 42 g/mol contains 85.7% carbon and 14.3% hydrogen by mass. The formula of this molecule suggests the following skeleton. Draw lewis structures for molecules. In this case, we can condense the last few steps, since not all of them. Web we can draw the lewis structure of any covalent molecule by following the six steps discussed earlier. No one rated this answer yet — why not be the first? Here’s how to approach this question. Consider formaldehyde (h 2 co) which contains 12 valence electrons. A compound with a molar mass of about 42 g/mol contains 85.7% carbon and 14.3% hydrogen by mass. We also use lewis symbols to indicate. Draw lewis structures for molecules. Carbon (c) has 4 valence electrons and sulfur (s) has 6 valence electrons. 100% (21 ratings) share share. Draw out the molecular backbone of the compound. A compound with a molar mass of about 42 g/mol contains 85.7% carbon and 14.3% hydrogen by mass. Draw lewis structures depicting the bonding in simple molecules. Web write the lewis structure for a molecule of the compound. Web we can draw the lewis structure of any covalent molecule by following the six steps discussed earlier. Carbon monosulfide is an organosulfur compound. Two arrangements of atoms are possible for a compound with a molar mass of about 45 g/mol that contains 52.2% c, 13.1% h, and 34.7% o by mass. Web writing lewis structures for diatomic molecules draw. The following procedure can be used to construct lewis electron structures for simple molecules. Consider formaldehyde (h 2 co) which contains 12 valence electrons. There are 4 valence electrons in an atom of c and 6 valence. Count the number of valence electrons for both carbon and sulfur to determine how many electrons you have to work with in creating. Web writing lewis structures for diatomic molecules draw the lewis structure for a carbon monosulfide (cs) molecule. A compound with a molar mass of about 42 g/mol contains 85.7% carbon and 14.3% hydrogen by mass. A lewis structure is a diagram that shows the chemical bonds between atoms in a. Draw a single line (representing a pair of. Web there. Count the number of valence electrons for both carbon and sulfur to determine how many electrons you have to work with in creating the lewis structure. Web write the lewis structure for a molecule of the compound. Two arrangements of atoms are possible for a compound with a molar mass of about 45 g/mol that contains 52.2% c, 13.1% h,. Draw a single line (representing a pair of. Before we can begin drawing the lewis structure for cos ( carbon monosulfide ), we need to determine. For very simple molecules and molecular ions, we can write the lewis. Draw out the molecular backbone of the compound. This is probably the most difficult step in drawing lewis structures because we must. Before we can begin drawing the lewis structure for cos ( carbon monosulfide ), we need to determine. Web we can draw the lewis structure of any covalent molecule by following the six steps discussed earlier. 2(1) + 4 + 6 = 12. For very simple molecules and molecular ions, we can write the lewis. Web draw lewis structures for. The formula of this molecule suggests the following skeleton. Web carbon monosulfide is a diatomic molecule composed of carbon and sulfur elements combined in a ratio of 1:1. This problem has been solved! Carbon monosulfide is an organosulfur compound. Web here are the steps to draw a lewis structure. Web draw a plausible lewis electron structure for a compound with the molecular formula cl 3 po. 100% (21 ratings) share share. This diatomic molecule is the sulfur analogue of carbon monoxide, and is unstable as a solid or a. Draw a single line (representing a pair of. Add/replace, change length/angle, or erase. Consider formaldehyde (h 2 co) which contains 12 valence electrons. Carbon monosulfide is an organosulfur compound. From a condensed molecular formula, you obtain information about which atoms are connected to each. No one rated this answer yet — why not be the first? Web carbon monosulfide is a chemical compound with the formula cs. A compound with a molar mass of about 42 g/mol contains 85.7% carbon and 14.3% hydrogen by mass. Before we can begin drawing the lewis structure for cos ( carbon monosulfide ), we need to determine. The example is for the nitrate ion. For very simple molecules and molecular ions, we can write the lewis. Web there are three steps you should follow to draw a correct structure. Draw out the molecular backbone of the compound. Web we can draw the lewis structure of any covalent molecule by following the six steps discussed earlier. The formula of this molecule suggests the following skeleton. There are 4 valence electrons in an atom of c and 6 valence. In this case, we can condense the last few steps, since not all of them. Counting total valence electrons of atoms.
SOLVED Draw the Lewis structure for a carbon monosulfide (CS) molecule.

Lewis Diagram Of Carbon

Carbon Monosulfide Lewis Dot Structure bmptootles
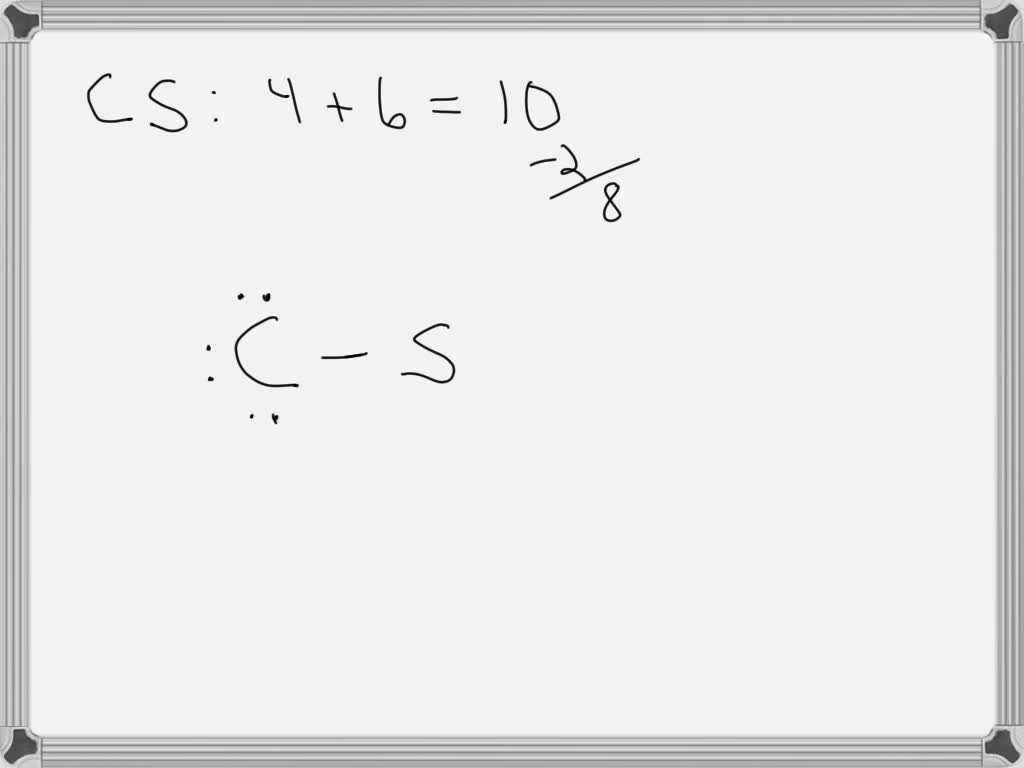
SOLVED Draw the Lewis structure for a carbon monosulfide (CS) molecule.

CS2 Lewis Structure How to Draw the Lewis Structure for CS2 YouTube

Drawing Lewis Dot Structures of Molecules
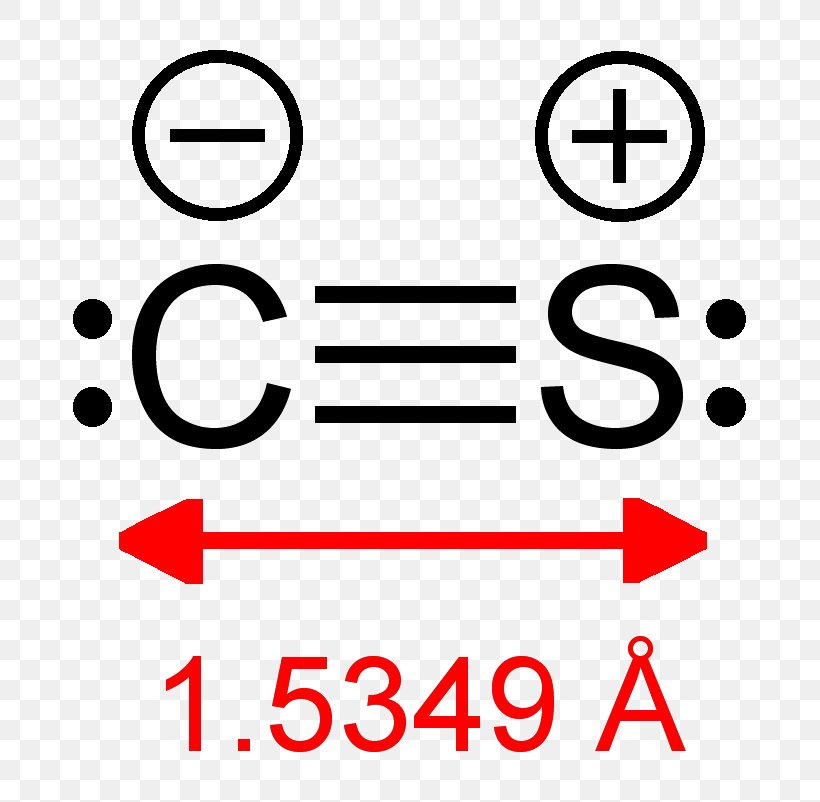
Carbon Monosulfide Lewis Structure Molecule Carbon Monoxide, PNG

FileCarbon Lewis Structure PNG.png Wikimedia Commons

How to Draw a Lewis Structure
Carbon Monosulfide Lewis Dot Structure bmptootles
This Diatomic Molecule Is The Sulfur Analogue Of Carbon Monoxide, And Is Unstable As A Solid Or A.
Web Carbon Monosulfide Is A Diatomic Molecule Composed Of Carbon And Sulfur Elements Combined In A Ratio Of 1:1.
Web Writing Lewis Structures For Diatomic Molecules Draw The Lewis Structure For A Carbon Monosulfide (Cs) Molecule.
Web Write The Lewis Structure For A Molecule Of The Compound.
Related Post: