How To Draw A Vector Diagram
How To Draw A Vector Diagram - Magnitude, direction, angle, physics, science. = (5 2) a → = ( 5 2) the vector b. I put an example below so you can see how it is done. 46 views 1 month ago #momentum #physics #grade12physics. Web how to draw a vector diagram from a space diagram. Vectors are geometric representations of magnitude and direction which are often represented by straight arrows, starting at one point on a coordinate axis and ending at a different point. Decide on a reference direction. Make sure that you fill in the arrow head. Make sure to separate the x and y value with a comma. Web vector diagrams can be used to resolve the pulling force into a horizontal component acting to the right, and a vertical component acting upwards. Decide upon a scale and write it down. Vectors are geometric representations of magnitude and direction which are often represented by straight arrows, starting at one point on a coordinate axis and ending at a different point. Determine the length of the arrow representing the vector, by using the scale. This tutorial video explains how to draw vector diagrams for. Web this video tutorial lesson discusses the method of drawing a vector to scale with the indicated magnitude and direction. Let's say my vector x, nice and bold x, is equal to, and i'm doing everything in r2, but in the last part of this video i'll make a few examples in r3 or r4. Web about press copyright contact. Fill in the magnitude of the vector. Using gridded paper, draw each of the following vectors: Web for example, use 1 cm = 10 m or 1 cm = 1 n, so that the diagram is around 10 cm high. In a vector diagram, the magnitude of a vector quantity is represented by the size of the vector arrow. It. Vectors are quantities that have both magnitude and direction, and they are typically represented as arrows. Web science is lit. It also demonstrates how to determine the magnitude and direction of a vector in a scaled vector diagram. The physics classroom explains how to. Let's say my vector x, nice and bold x, is equal to, and i'm doing everything. Web vector diagrams can be used to resolve the pulling force into a horizontal component acting to the right, and a vertical component acting upwards. This is the resultant , or the sum, of the vectors. This tutorial video explains how to draw vector diagrams for momentum problems. = (1 6) g → = ( 1 6) the vector h.. Let's say my vector x, nice and bold x, is equal to, and i'm doing everything in r2, but in the last part of this video i'll make a few examples in r3 or r4. Web vector diagrams depict a vector by use of an arrow drawn to scale in a specific direction. How to find the resultant vector. Web. Let's say my vector x, nice and bold x, is equal to, and i'm doing everything in r2, but in the last part of this video i'll make a few examples in r3 or r4. Web to add the vectors (x₁,y₁) and (x₂,y₂), we add the corresponding components from each vector: = (−2 −5) e → = ( − 2. Web how to draw a vector diagram from a space diagram. Learn how to draw vector. Figure 5.5 the diagram shows the resultant vector, a ruler, and protractor. Decide on a reference direction. Web © 2024 google llc. Web © 2024 google llc. Decide on a reference direction. Use the scale factor to calculate the magnitude. There's also a nice graphical way to add vectors, and the two ways will always result in the same vector. Web vector diagrams depict a vector by use of an arrow drawn to scale in a specific direction. Web vector diagrams can be used to resolve the pulling force into a horizontal component acting to the right, and a vertical component acting upwards. = (0 5) d → = ( 0 5) the vector e. Let's say my vector x, nice and bold x, is equal to, and i'm doing everything in r2, but in the last part. Web so now that we have that notion, we can kind of start understanding the idea of subtracting vectors. Web drawing vector diagrams.physics lecture #7.for a pdf transcript of this lecture, go to www.richardlouie.com. Draw the vector as an arrow. = (5 2) a → = ( 5 2) the vector b. Let me make up 2 new vectors right now. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. = (−4 0) f → = ( − 4 0) the vector g. Without any additional vectors, a generic 3d coordinate system can be seen in figure 5.3.1. = (−2 −5) e → = ( − 2 − 5) the vector f. There's also a nice graphical way to add vectors, and the two ways will always result in the same vector. I put an example below so you can see how it is done. The sum of (2,4) and (1,5) is (2+1,4+5), which is (3,9). Web science is lit. Decide upon a scale and write it down. = (1 6) g → = ( 1 6) the vector h. We start with the basics of drawing a vector in 3d.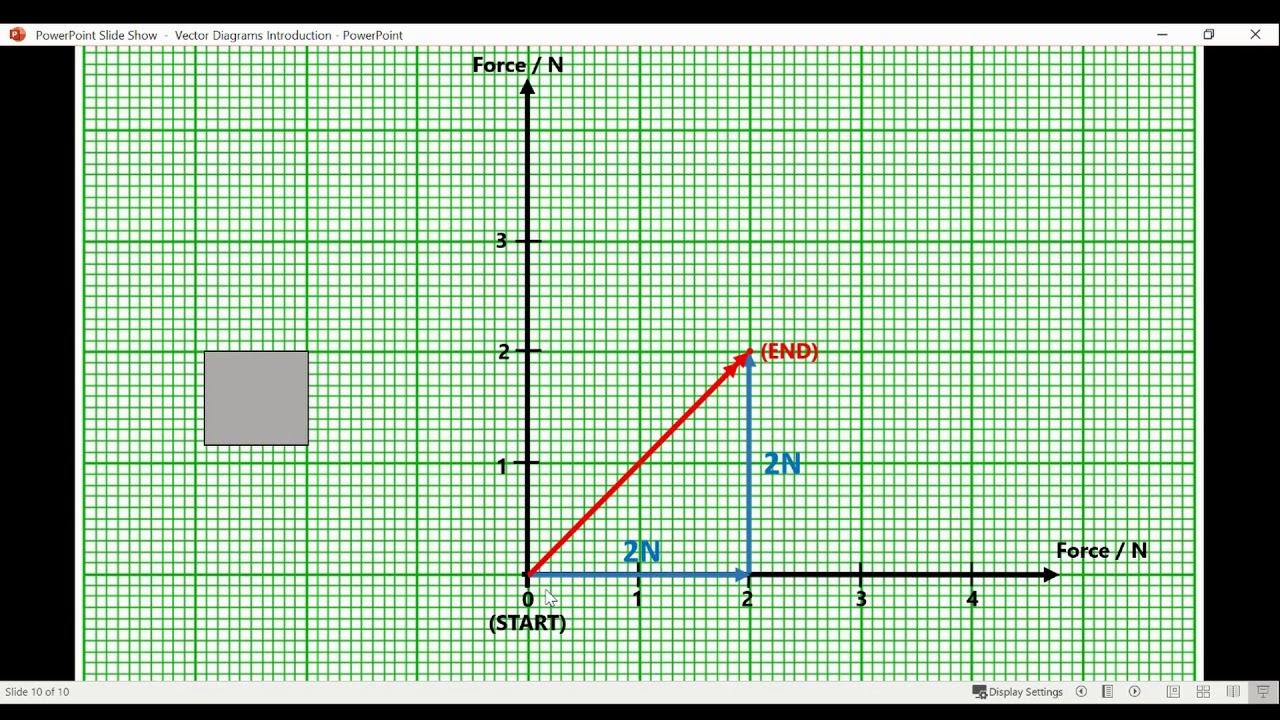
Introduction to Vector Diagrams Vector Diagrams Series (Part 1) YouTube
How To Draw A Vector Diagram Physics

Introduction to Vectors Definitions Components How to Draw a

Vector Diagram in Physics Addition, Subtraction & Examples Video
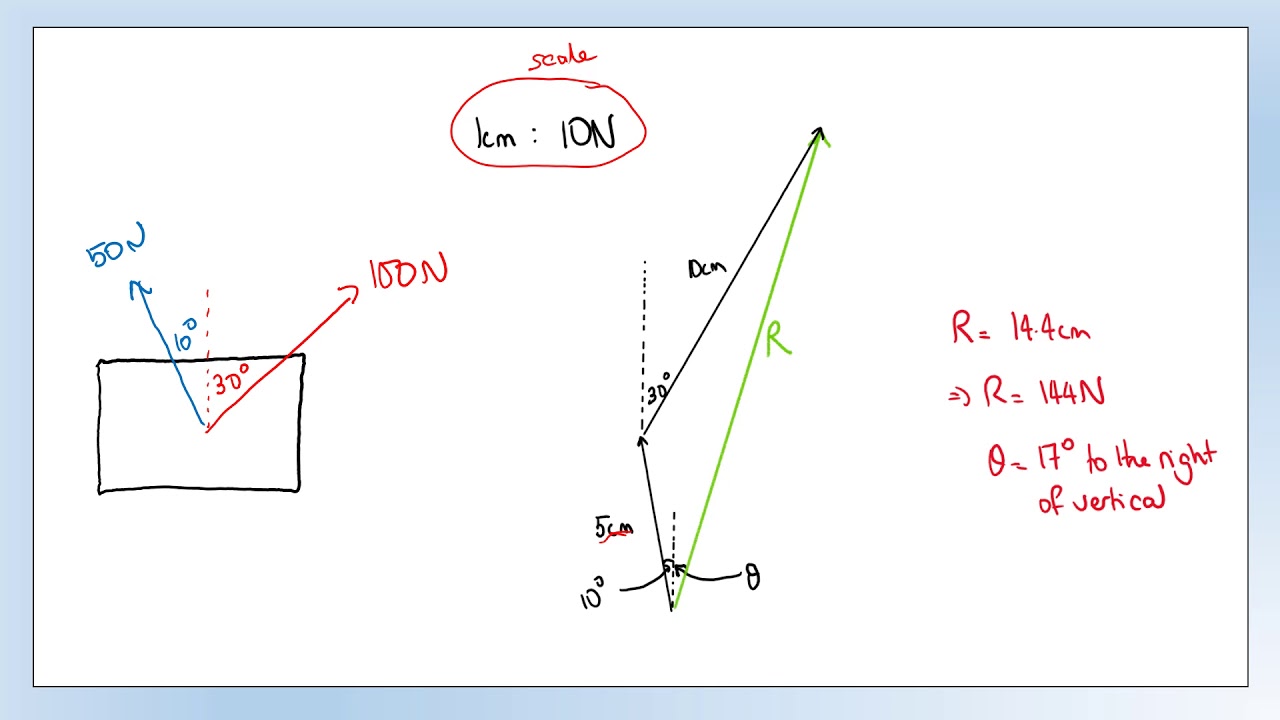
GCSE Physics Adding vectors in 2 dimensions YouTube

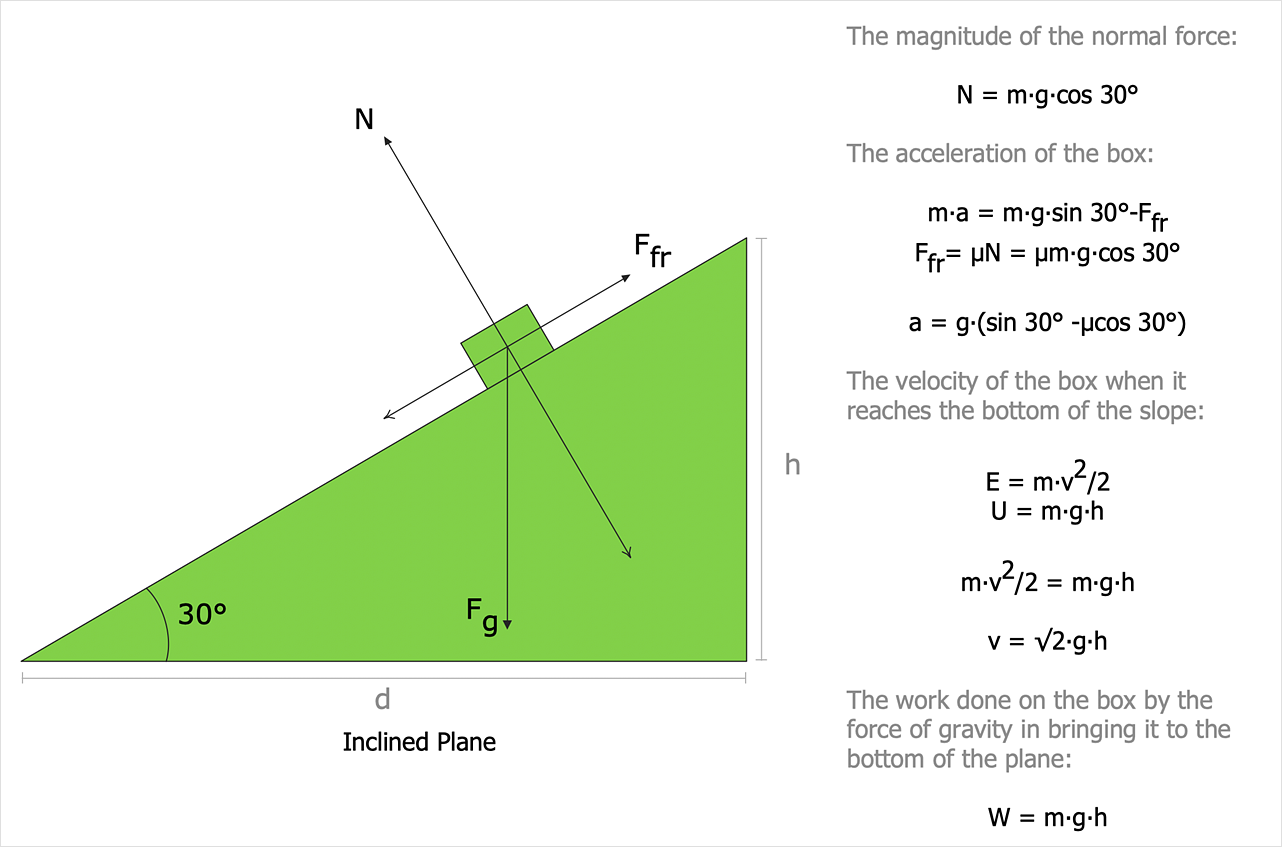
Components of a Vector Formula, Applications, Examples
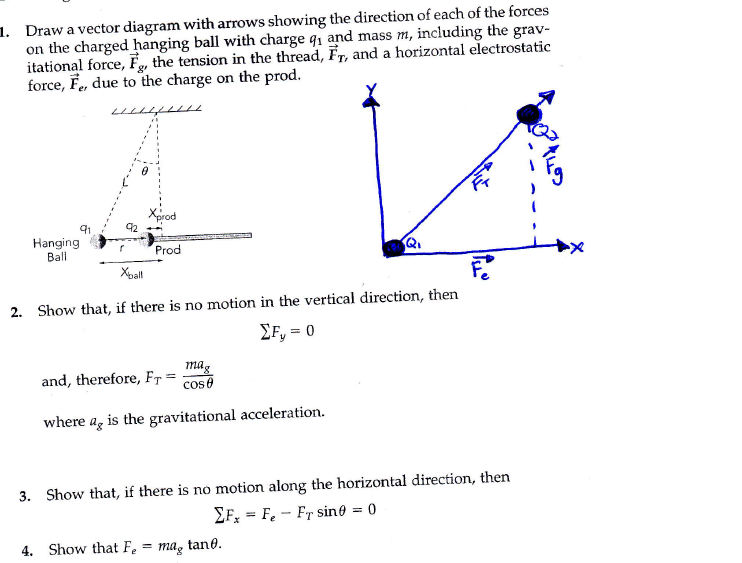
Solved Draw a vector diagram with arrows showing the

AQA P2 Force Vector Diagrams (GCSE) YouTube
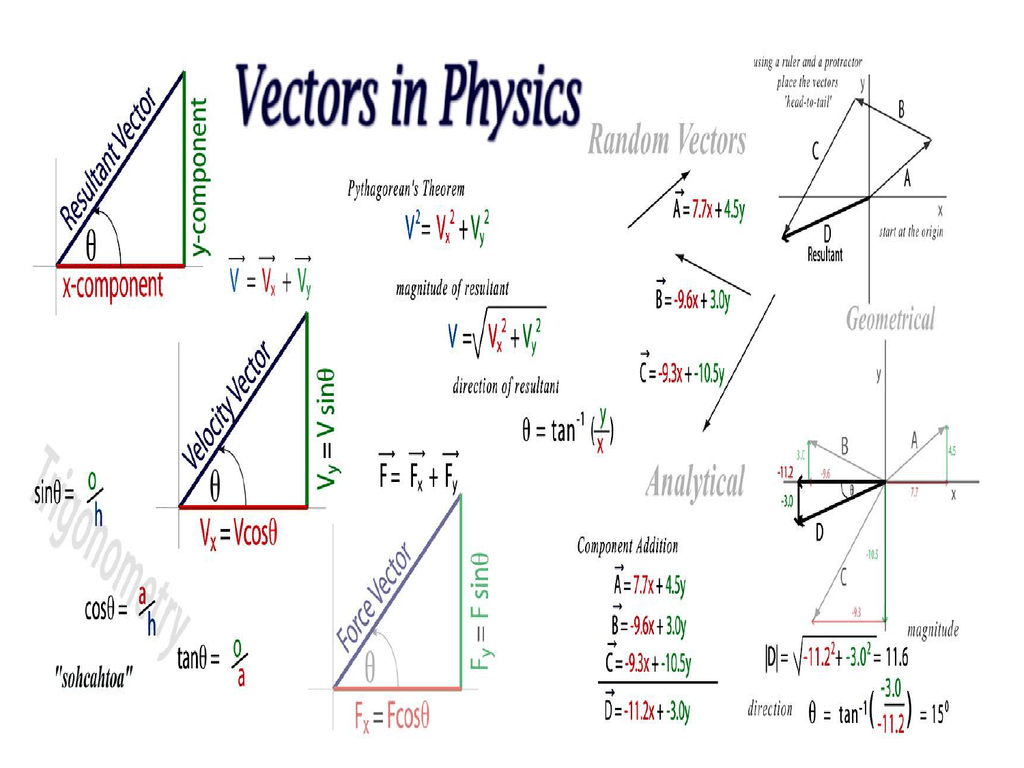
How To Draw A Vector Diagram Physics

Draw a vector in standard position, or anywhere YouTube
Vectors Are Quantities That Have Both Magnitude And Direction, And They Are Typically Represented As Arrows.
He Moved The Tail Of One Vector To The Head Of The Other Because That Is The Geometric Way Of Looking At What It Means To Add Vectors.
Or Just Not Sure How To Use Such A Vector Diagram?
Draw The Vectors At Right Angles To One Another.
Related Post: