How To Draw Resonance Structures In Organic Chemistry
How To Draw Resonance Structures In Organic Chemistry - Web when learning to draw and interpret resonance structures, there are a few basic guidelines to help. Web draw three resonance forms for the pentadienyl radical, where a radical is a substance that contains a single, unpaired electron in one of its orbitals, denoted by a dot (·). How to find the best resonance structure by applying electronegativity; Acids, bases & electron flow. This system will also be used to help describe how electrons from in reactions. 1) when you see two different resonance contributors, you are not seeing a chemical reaction! This movement of the electrons is called delocalization. 1) there is only one real structure for each molecule or ion. Here we will focus on how to draw resonance structures (or resonance contributors) for organic chemistry species, and how to compare the relative stabilities between the structures. Evaluating resonance structures with positive charge; Web the discussion of resonance effect heavily relies on the understanding of resonance structures. Evaluating resonance structures with positive charge; Web as we’ve seen in previous posts, four key factors that determine the importance of resonance structures in organic chemistry are: Rather, you are seeing the exact same molecule or ion depicted in two different ways. Resonance is a way. Web rules for drawing resonance structures: How stable are the negative charges? There is no change in hybridization between the structures. Delocalization and resonance structures rules. Evaluating resonance structures with negative charges; An animation of how one can do a resonance with ozone by moving electrons. Resonance is a way of describing delocalized electrons within certain molecules or polyatomic ions where the bonding cannot be expressed by a single lewis formula. Sometimes one dot structures is not enough to completely describe a molecule or an ion, sometimes you need two or more,. Web when learning to draw and interpret resonance structures, there are a few basic guidelines to help. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Curved double barbed arrows indicates the flow of two electrons. Web resonance structures and hybridization (video) | khan academy. How stable are the positive charges? Web learn how to draw its resonance, as well as resonance intermediates for substituted aromatic compounds including electron donating groups which resonate into the ring and electron withdrawing groups which cause resonance out of the ring. It explains how to draw the resonance structures using curved. How to find the best resonance structure by applying electronegativity; Web the discussion of. This movement of the electrons is called delocalization. Resonance structures, hybridization of orbitals, and localized and delocalized electron density. Web draw three resonance forms for the pentadienyl radical, where a radical is a substance that contains a single, unpaired electron in one of its orbitals, denoted by a dot (·). This real structure (the resonance hybrid) takes its character from. In order to draw the resonance structures, one has to keep the following rules in mind: Web the discussion of the resonance effect heavily relies on the understanding of resonance structures. Web when learning to draw and interpret resonance structures, there are a few basic guidelines to help. Web draw three resonance forms for the pentadienyl radical, where a radical. Only electrons move through the molecules. They must have the same number of electrons. An animation of how one can do a resonance with ozone by moving electrons. We need to draw another resonance structure. Consider ozone (o 3) solution. This system will also be used to help describe how electrons from in reactions. This is the acetate anion, and this dot structure does not completely describe the acetate anion; Acids, bases & electron flow. A molecule or ion with such delocalized electrons is represented by several resonance structures. Curved double barbed arrows indicates the flow of two electrons. There are two simple answers to this question: Web draw three resonance forms for the pentadienyl radical, where a radical is a substance that contains a single, unpaired electron in one of its orbitals, denoted by a dot (·). In resonance structures, the electrons are able to move to help stabilize the molecule. A molecule or ion with such delocalized. There are two simple answers to this question: It explains how to draw the resonance structures using curved. Rather, you are seeing the exact same molecule or ion depicted in two different ways. Evaluating resonance structures with negative charges; Delocalization and resonance structures rules. This system will also be used to help describe how electrons from in reactions. Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and more. Resonance structures, hybridization of orbitals, and localized and delocalized electron density. Web the discussion of the resonance effect heavily relies on the understanding of resonance structures. How stable are the positive charges? Sometimes one dot structures is not enough to completely describe a molecule or an ion, sometimes you need two or more, and here's an example: This real structure (the resonance hybrid) takes its character from the average of all the individual resonance contributors. 602k views 2 years ago new organic chemistry playlist. Here, we will focus on how to draw resonance structures (or resonance contributors) for organic chemistry species and how to compare the relative stabilities between the structures. This is the acetate anion, and this dot structure does not completely describe the acetate anion; Web organic chemistry has developed a system to show how electrons move between resonance structures.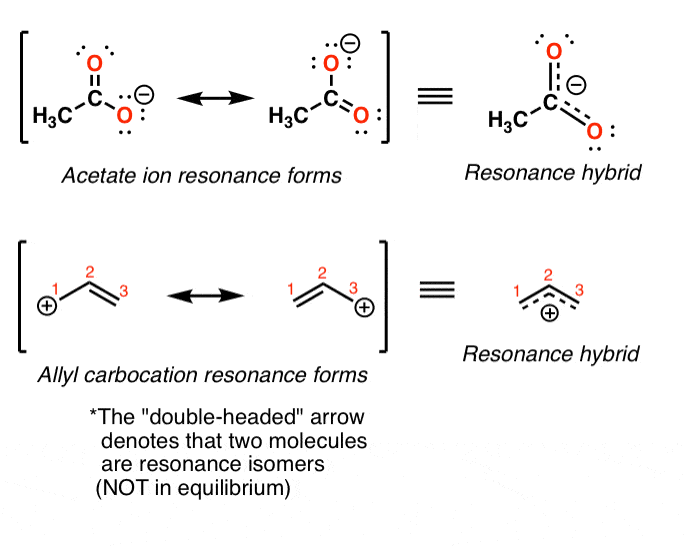
Resonance Structures 4 Rules On How To Evaluate Them, With Practice

Resonance Structures YouTube
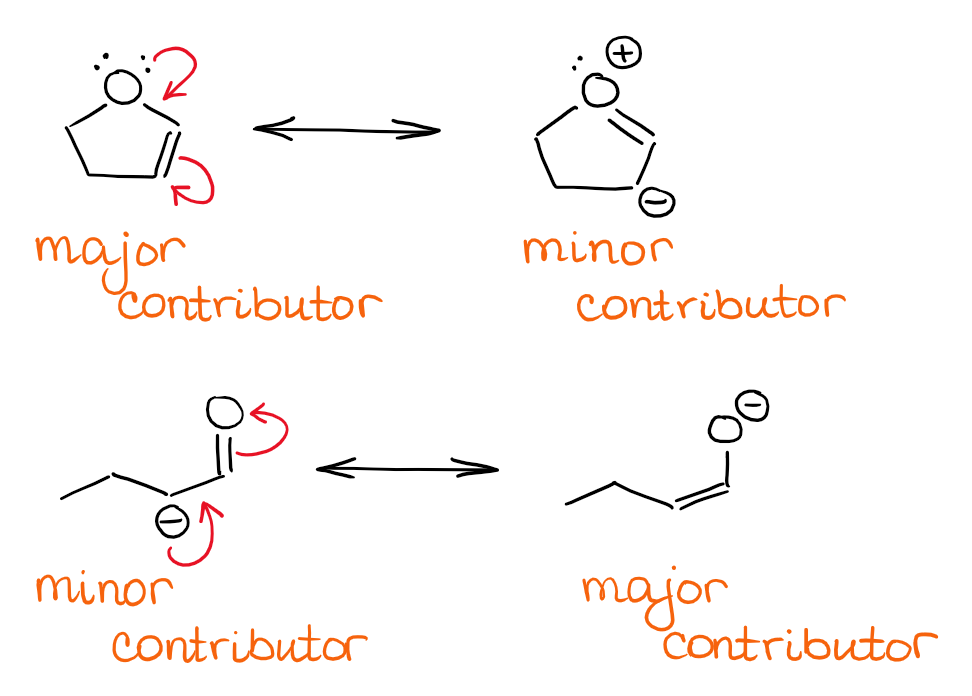
Resonance in Organic Chemistry — Organic Chemistry Tutor
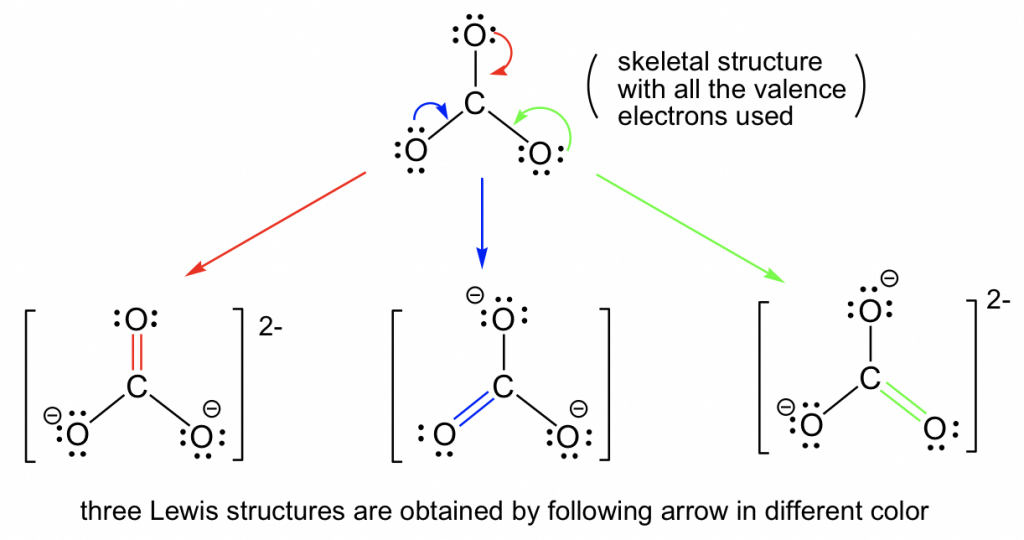
1.3 Resonance Structures Organic Chemistry I

How to Draw Resonance Contributors MCC Organic Chemistry
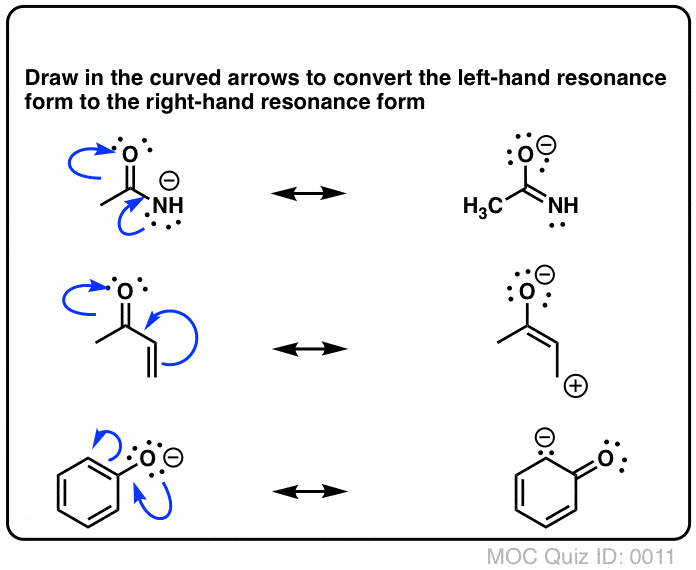
Resonance Structures Practice Master Organic Chemistry
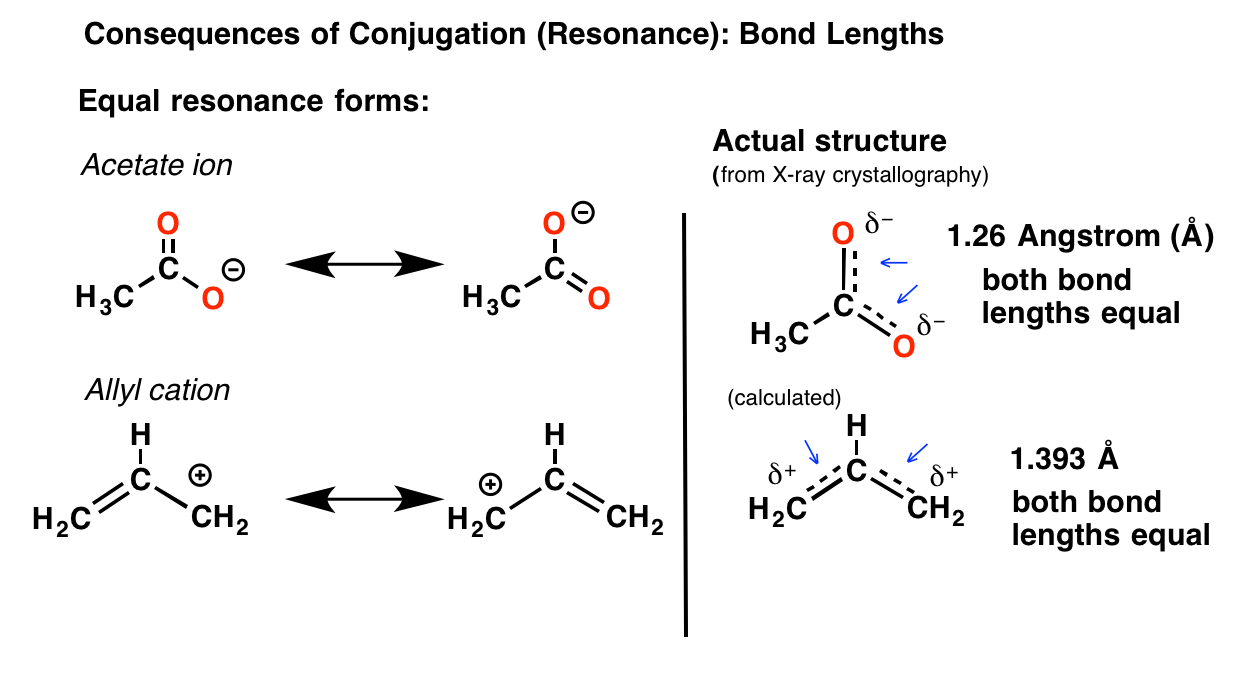
Conjugation And Resonance In Organic Chemistry
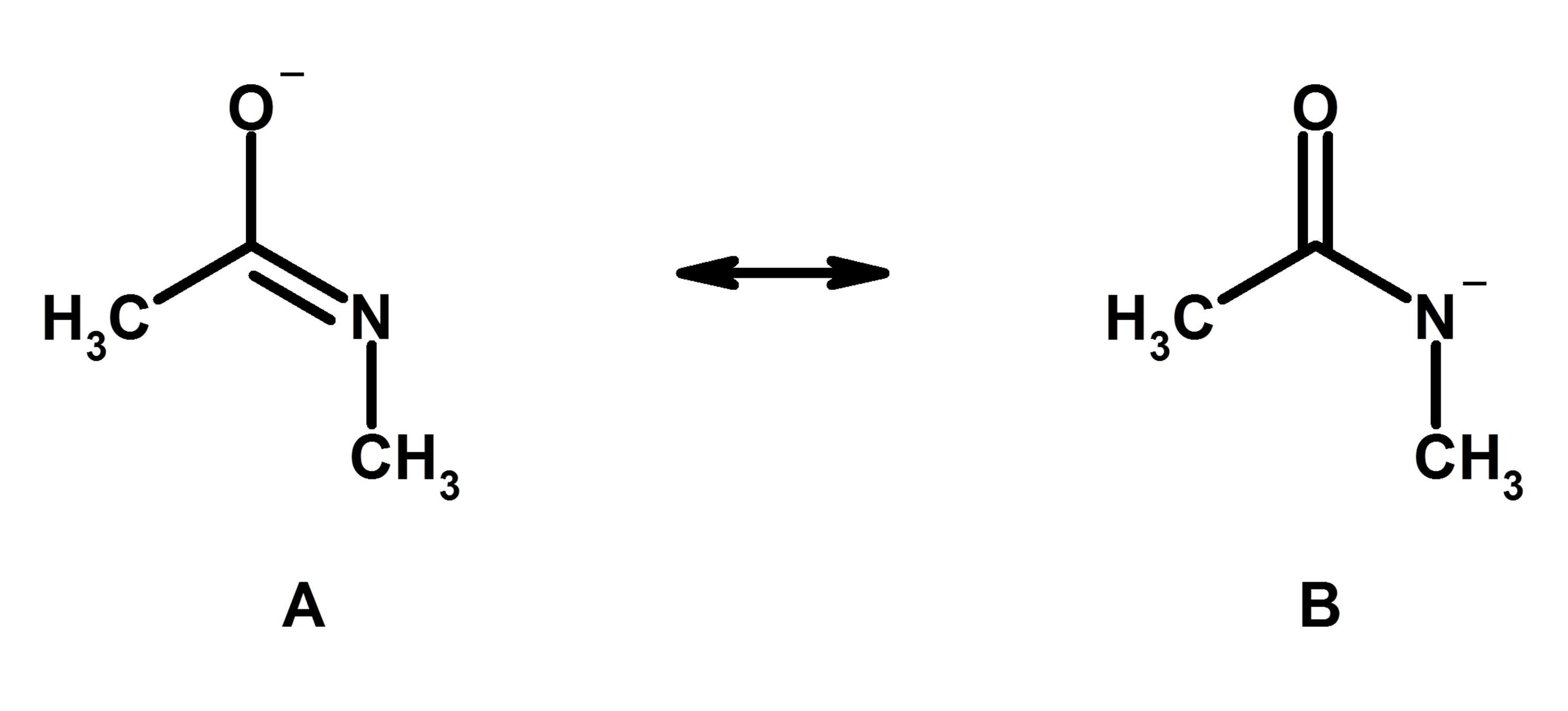
Trick 11 Master Organic Chemistry Resonance Structures

6.2. Resonance Organic Chemistry 1 An open textbook
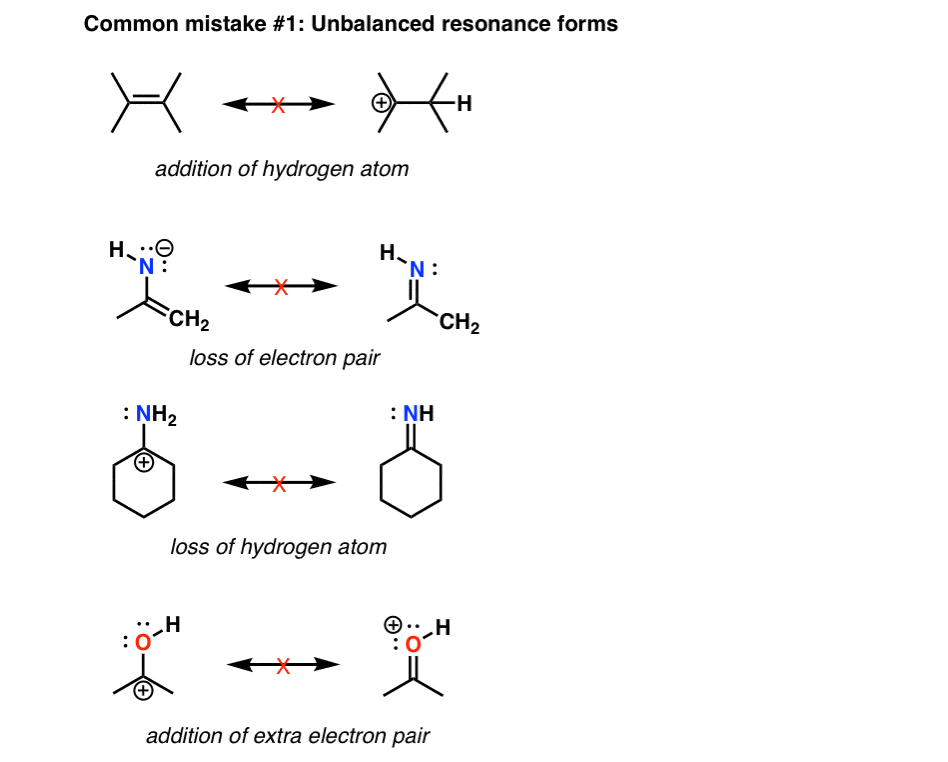
Drawing Resonance Structures 3 Common Mistakes To Avoid
Web Rules For Drawing Resonance Structures:
In Order To Draw The Resonance Structures, One Has To Keep The Following Rules In Mind:
1) There Is Only One Real Structure For Each Molecule Or Ion.
Web Resonance Structures Are A Set Of Two Or More Lewis Structures That Collectively Describe The Electronic Bonding Of A Single Polyatomic Species Including Fractional Bonds And Fractional Charges.
Related Post: