Hyaline Cartilage Tissue Drawing
Hyaline Cartilage Tissue Drawing - Hyaline cartilage with and without illustration overlay. It is avascular and its microarchitecture is less organized than bone. Web the hyaline cartilage in the trachea is in the middle of the tracheal wall. 35 views 4 months ago histology discussion, viva, oral questions. Learn more about how pressbooks supports open publishing practices. Web the illustrative book of cartilage repair. Check out our youtube video to help you understand hyaline cartilage: Isogenous groups and interstitial growth results when chondrocytes divide and produce extracellular matrix. Slide 2, trachea (h&e) on slide 2, trachea (h&e), identify the hyaline cartilage which provides support for the softer tracheal tissues. Web hyaline cartilage, the most common type of cartilage, is composed of type ii collagen and chondromucoprotein and often has a glassy appearance. Web the illustrative book of cartilage repair. New articular cartilage is limited to interstitial growth because of the. Territorial matrix lies immediately around each. Web hyaline cartilage, the most common type of cartilage, is composed of type ii collagen and chondromucoprotein and often has a glassy appearance. Web during embryonic development, hyaline cartilage serves as temporary cartilage models that are. Slide 2, trachea (h&e) on slide 2, trachea (h&e), identify the hyaline cartilage which provides support for the softer tracheal tissues. It is avascular and its microarchitecture is less organized than bone. Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue that differs from bone in several ways; Web during embryonic development, hyaline cartilage serves as temporary cartilage models that are essential precursors. Check out our youtube video to help you understand hyaline cartilage: Watch the video tutorial now. Although hyaline cartilage feels nearly as hard and dense as bone. Web hyaline cartilage, the most common type of cartilage, is composed of type ii collagen and chondromucoprotein and often has a glassy appearance. Slide 2, trachea (h&e) on slide 2, trachea (h&e), identify. Tamás oláh, tunku kamarul, henning madry & malliga raman murali. Most of the image is occupied by a section. New articular cartilage is limited to interstitial growth because of the. Watch the video tutorial now. Isogenous groups and interstitial growth results when chondrocytes divide and produce extracellular matrix. It is avascular and its microarchitecture is less organized than bone. Isogenous groups and interstitial growth results when chondrocytes divide and produce extracellular matrix. Web articular cartilage is a remnant of the hyaline cartilage that formed the template for the developing bone. The video shows the details of how to draw the microscopic structure of. Watch the video tutorial now. Watch the video tutorial now. It is typically characterized by a firm consistency and a smooth surface. Territorial matrix lies immediately around each. Web articular cartilage is a remnant of the hyaline cartilage that formed the template for the developing bone. Web hyaline cartilage is a supportive connective tissue with a rigid yet slightly flexible extracellular matrix. Web hyaline cartilage is the most common type of cartilage in the human body. The video shows the details of how to draw the microscopic structure of. It is typically characterized by a firm consistency and a smooth surface. A higher magnification of the wall of the trachea shows the lumen with its epithelial lining in the lower left of. It is avascular and its microarchitecture is less organized than bone. Web hyaline cartilage is a supportive connective tissue with a rigid yet slightly flexible extracellular matrix. New articular cartilage is limited to interstitial growth because of the. Learn more about how pressbooks supports open publishing practices. Most of the image is occupied by a section. A histological overview of the most common type of cartilage in the human body. Watch the video tutorial now. Web hyaline cartilage, the most common type of cartilage, is composed of type ii collagen and chondromucoprotein and often has a glassy appearance. The lack of blood vessels in hyaline cartilage means that nutrients and. Web during embryonic development, hyaline cartilage. Territorial matrix lies immediately around each. Most of the image is occupied by a section. Web the hyaline cartilage in the trachea is in the middle of the tracheal wall. The lack of blood vessels in hyaline cartilage means that nutrients and. Learn more about how pressbooks supports open publishing practices. Web hyaline cartilage, the most common type of cartilage, is composed of type ii collagen and chondromucoprotein and often has a glassy appearance. It is typically characterized by a firm consistency and a smooth surface. Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue that differs from bone in several ways; Web hyaline cartilage is the most common type of cartilage in the human body. Web articular cartilage is a remnant of the hyaline cartilage that formed the template for the developing bone. Learn more about how pressbooks supports open publishing practices. Web want to create or adapt books like this? The lack of blood vessels in hyaline cartilage means that nutrients and. It is avascular and its microarchitecture is less organized than bone. Web during embryonic development, hyaline cartilage serves as temporary cartilage models that are essential precursors to the formation of most of the axial and. Hyaline cartilage with and without illustration overlay. Web likecomment share subscribe #hyalinecartilage #histodiagrams #hyalinecartilagediagram #cartilagehistology The video shows the details of how to draw the microscopic structure of. Tamás oláh, tunku kamarul, henning madry & malliga raman murali. Although hyaline cartilage feels nearly as hard and dense as bone. Web the hyaline cartilage in the trachea is in the middle of the tracheal wall.
How to Draw Hyaline Cartilage Simple and easy steps Biology Exam

Hyaline cartilage structure and biochemical composition. Schematic

Mammal. Hyaline cartilage. Transverse section. 250X Hyaline cartilage
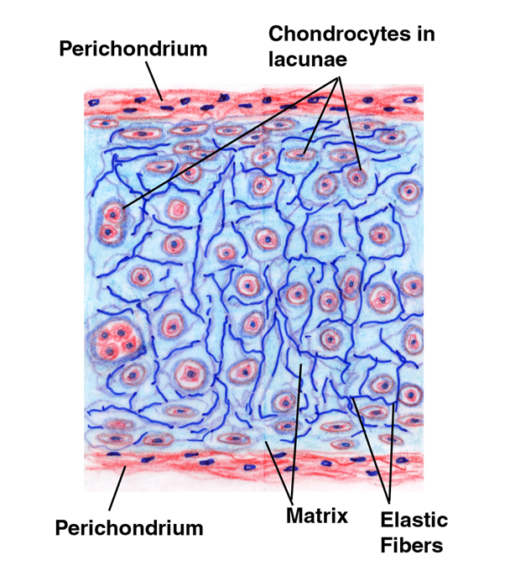
Hyaline cartilage Definition and Examples Biology Online Dictionary

Histology Image Cartilage

Connective Tissue Anatomy and Physiology
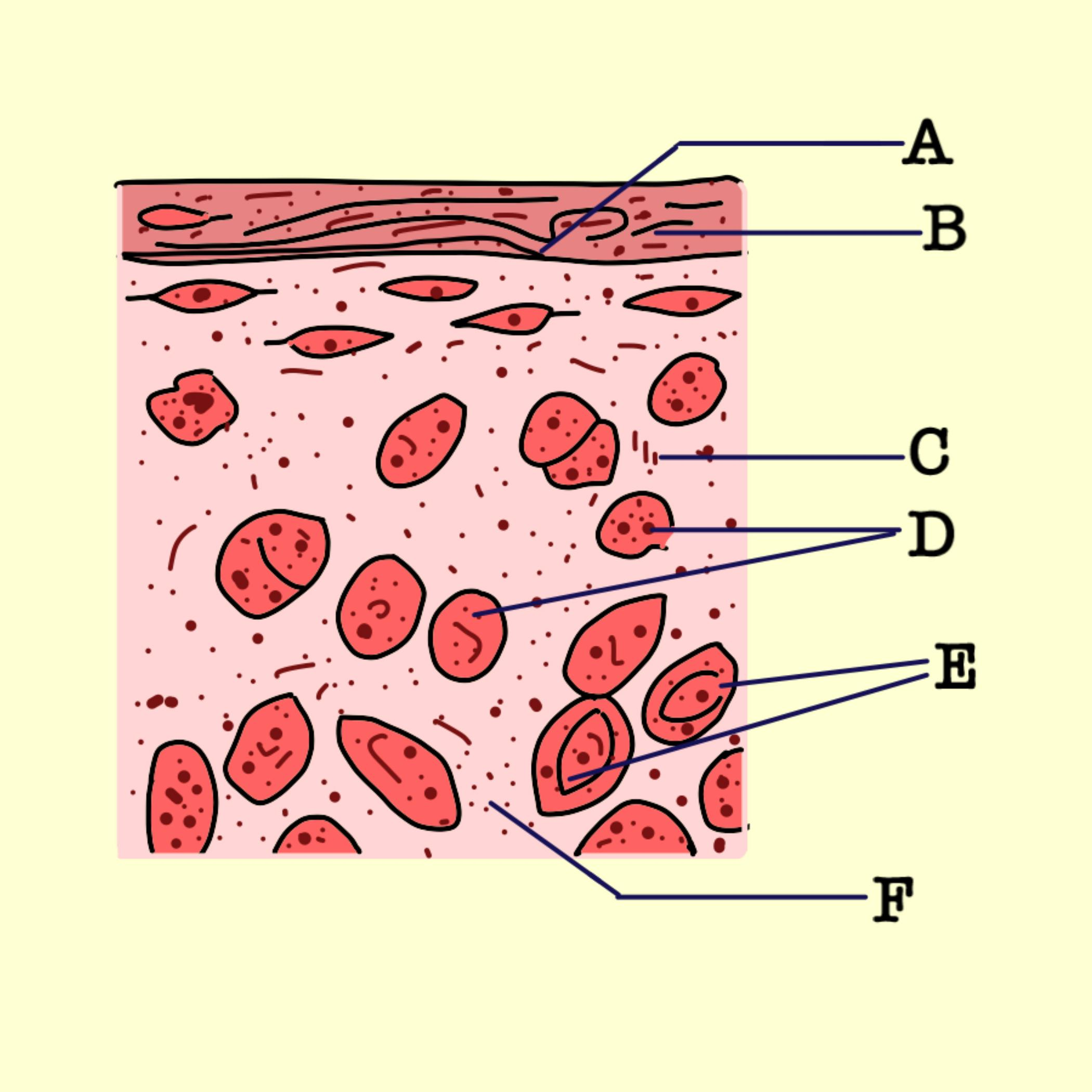
Hyaline Cartilage Connective Tissue Labeled

Illustrations Hyaline Cartilage General Histology

Perichondrium as hyaline, fibrous and elastic cartilage membrane
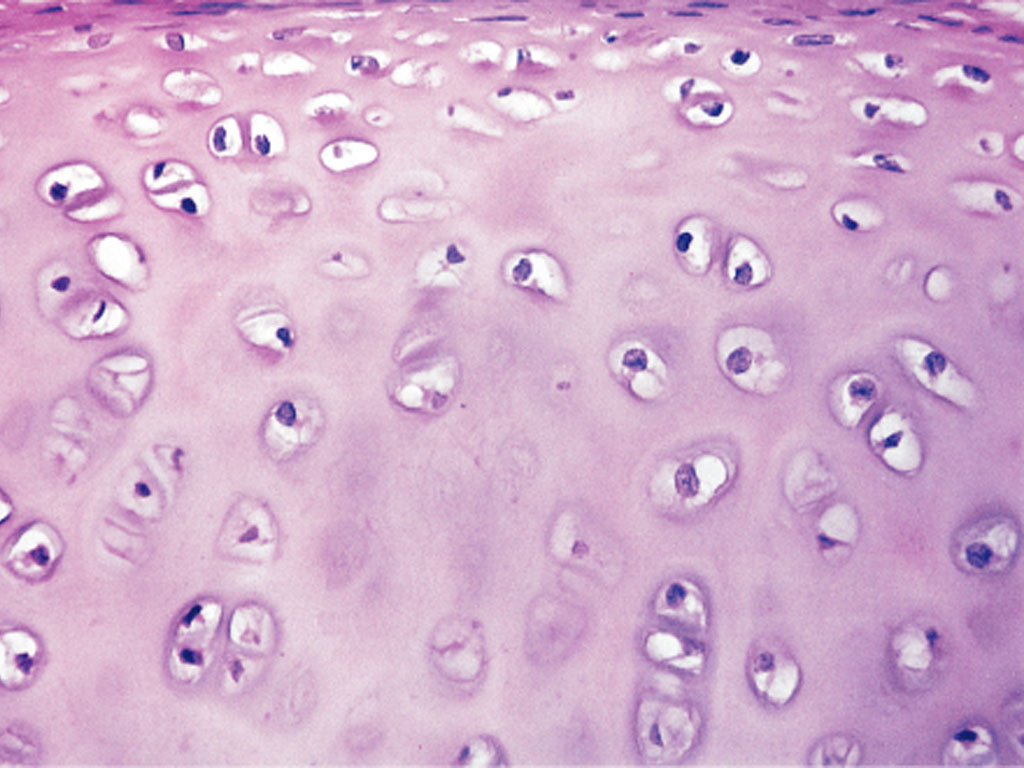
Hyaline Cartilage
Slide 2, Trachea (H&E) On Slide 2, Trachea (H&E), Identify The Hyaline Cartilage Which Provides Support For The Softer Tracheal Tissues.
Watch The Video Tutorial Now.
Web Hyaline Cartilage Is A Supportive Connective Tissue With A Rigid Yet Slightly Flexible Extracellular Matrix.
Web The Illustrative Book Of Cartilage Repair.
Related Post: