Nucleic Acids Drawing
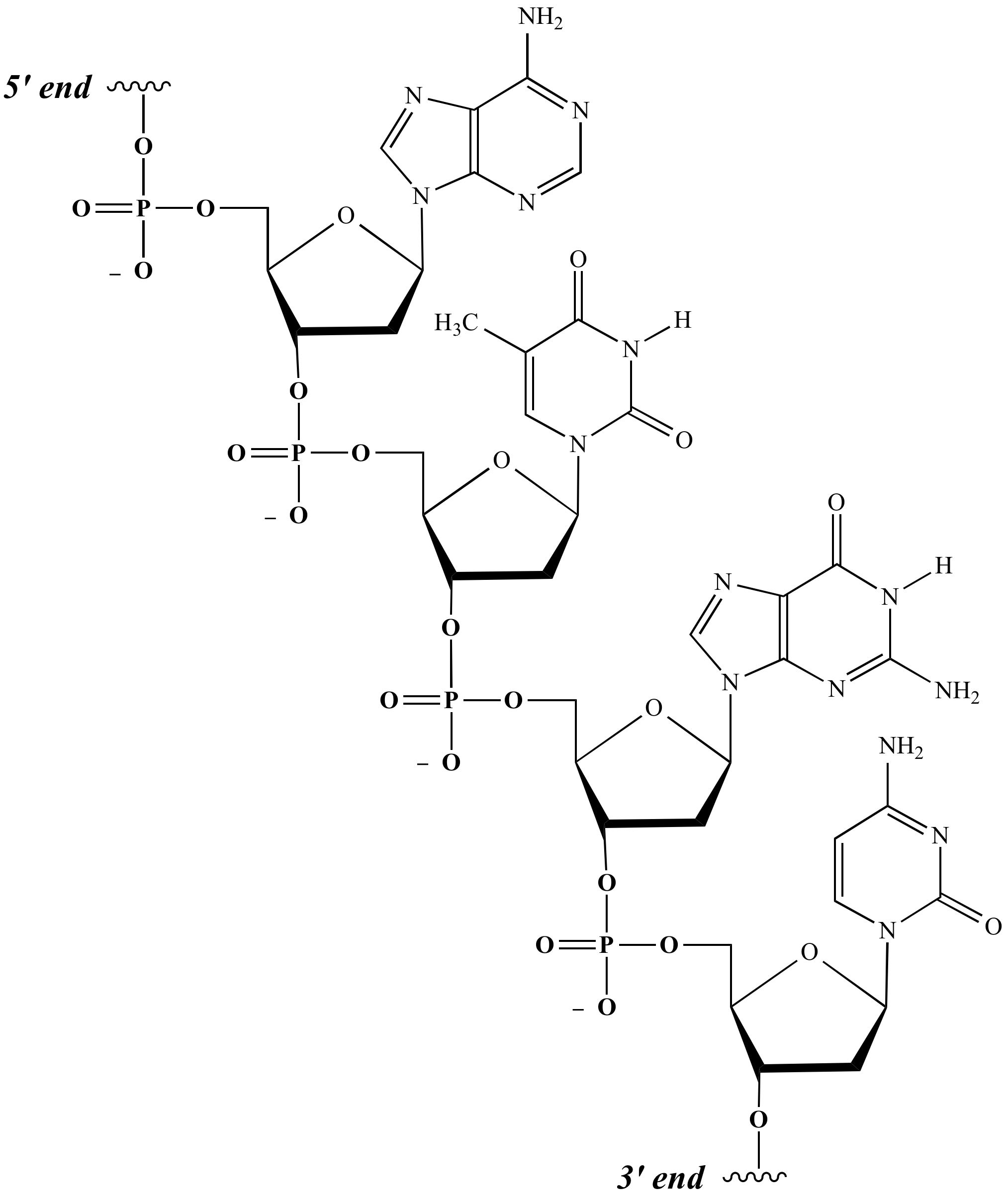
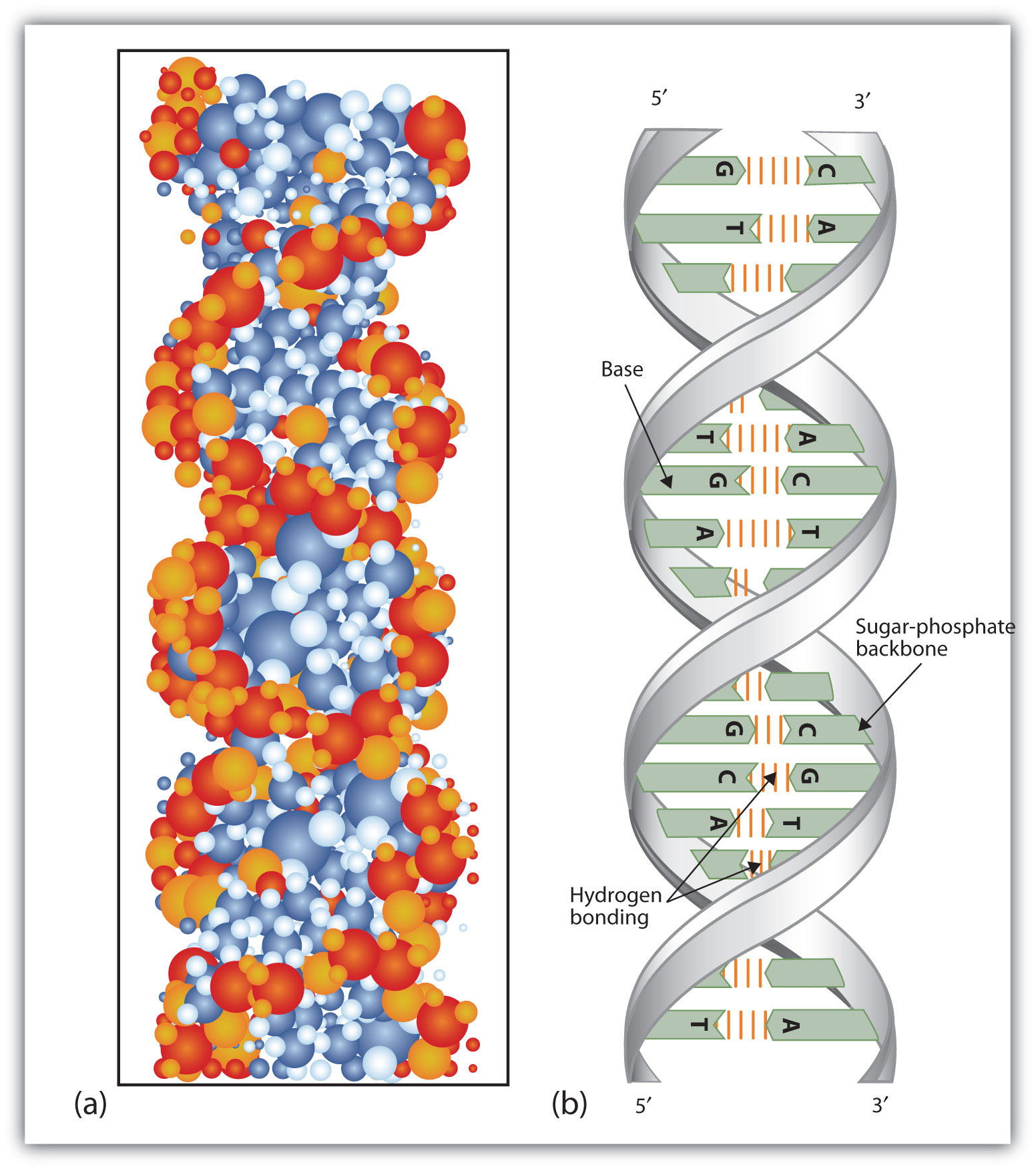
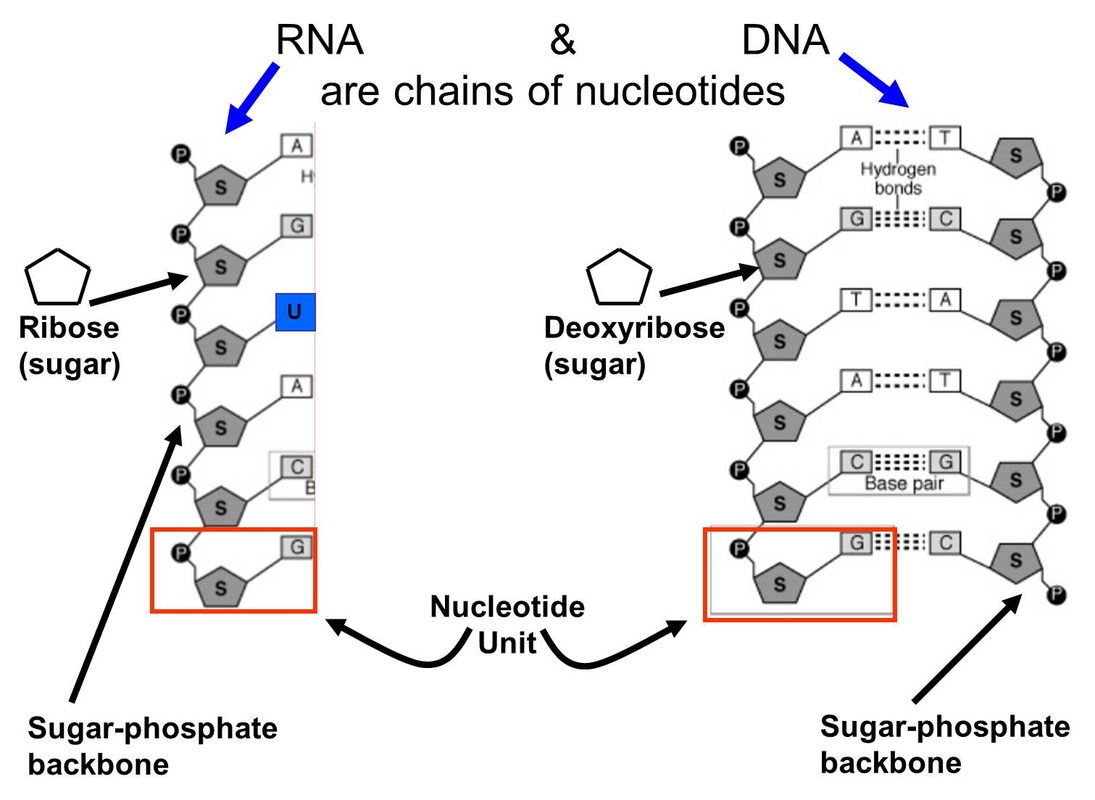
Nucleic Acids Drawing - Dna and rna, composed of nucleotide building blocks, store hereditary information. Dna belongs to a class of organic molecules called nucleic acids. Web the nucleic acids are vital biopolymers found in all living things, where they function to encode, transfer, and express genes.these large molecules are called nucleic acids because they were first identified inside the nucleus of cells, however, they are also found in mitochondria and chloroplasts as well as bacteria and viruses. Web our genetic information is coded within the macromolecule known as deoxyribonucleic acid (dna). Web nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life. Make certain that you can define, and use in context, the key terms below. Phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogen. Nucleic acids are polynucleotides—that is, long chainlike molecules composed of a series of nearly identical building blocks called nucleotides. It creates dna and rna, which store the information needed by cells to create proteins. Geometrically strict drawing of nucleic acid structures with graphical structure editing and highlighting of complementary subsequences. Phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogen. Web analogous nucleic acids in which the sugar component is ribose are termed ribonucleic acids, abbreviated rna. The ring contains one oxygen and four carbons. Nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life. It creates dna and rna, which store the information needed by cells to create proteins. Web describe the basic structure of nucleic acids. Web describe how a new copy of dna is synthesized. The deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) of a typical mammalian cell. The sugar in all four nucleotides is called deoxyribose. Web a nucleic acid is a chain of nucleotides which stores genetic information in biological systems. It creates dna and rna, which store the information needed by cells to create proteins. The four interfaces cover virtually all conceivable use cases. Web describe the basic structure of nucleic acids. The building block, or monomer, of all nucleic acids is a structure called a nucleotide. Web describe how a new copy of dna is synthesized. The acidic character of the nucleic acids was attributed to the phosphoric acid moiety. Web our genetic information is coded within the macromolecule known as deoxyribonucleic acid (dna). Web a web app for drawing and exploring nucleic acid structures. Dna belongs to a class of organic molecules called nucleic acids. Web like proteins, nucleic acids have a primary structure that. Roles of dna and rna in cells. The ring contains one oxygen and four carbons. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). Or open an rna 2d json schema. As depicted in the following drawing, the dna of a cell is tightly packed into chromosomes. This information is stored in multiple sets of. Primary structure consists of a linear sequence of nucleotides that are linked together by phosphodiester bond. It creates dna and rna, which store the information needed by cells to create proteins. The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). Nucleic acids, macromolecules made out of. Nucleic acids, macromolecules made out of units called nucleotides, come in two naturally occurring varieties: The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). It creates dna and rna, which store the information needed by cells to create proteins. Phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogen. The four interfaces cover virtually all conceivable use cases. First, the dna is wrapped around small proteins. Phosphate, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogen. Web describe how a new copy of dna is synthesized. Deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) nucleosides nucleotides. Deoxyribonucleic acid ( dna) and ribonucleic acid ( rna ). The two main types of nucleic acids are deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) and ribonucleic acid (rna). They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. A nucleotide has three parts: The ring contains one oxygen and four carbons. Unlike proteins, which have 20 different kinds of amino acids, there are only 4 different. Web the nucleic acids are vital biopolymers found in all living things, where they function to encode, transfer, and express genes.these large molecules are called nucleic acids because they were first identified inside the nucleus of cells, however, they are also found in mitochondria and chloroplasts as well as bacteria and viruses. The two main types of nucleic acids are. Nucleic acids, macromolecules made out of units called nucleotides, come in two naturally occurring varieties: Roles of dna and rna in cells. Nucleic acids are the most important macromolecules for the continuity of life. Sketch a section of nucleic acid to show how the nucleotide units are joined together. It creates dna and rna, which store the information needed by cells to create proteins. Web analogous nucleic acids in which the sugar component is ribose are termed ribonucleic acids, abbreviated rna. It is this linear sequence of nucleotides that make up the primary structure of dna or rna. Web our genetic information is coded within the macromolecule known as deoxyribonucleic acid (dna). They carry the genetic blueprint of a cell and carry instructions for the functioning of the cell. Dna and rna, composed of nucleotide building blocks, store hereditary information. Web a nucleic acid is a chain of nucleotides which stores genetic information in biological systems. Nucleic acids are polynucleotides—that is, long chainlike molecules composed of a series of nearly identical building blocks called nucleotides. The repeating, or monomer, units that are linked together to form nucleic acids are known as nucleotides. A nucleotide has three parts: The deoxyribonucleic acid (dna) of a typical mammalian cell. The nucleic acids, dna and rna, may be thought of as the information molecules of the cell.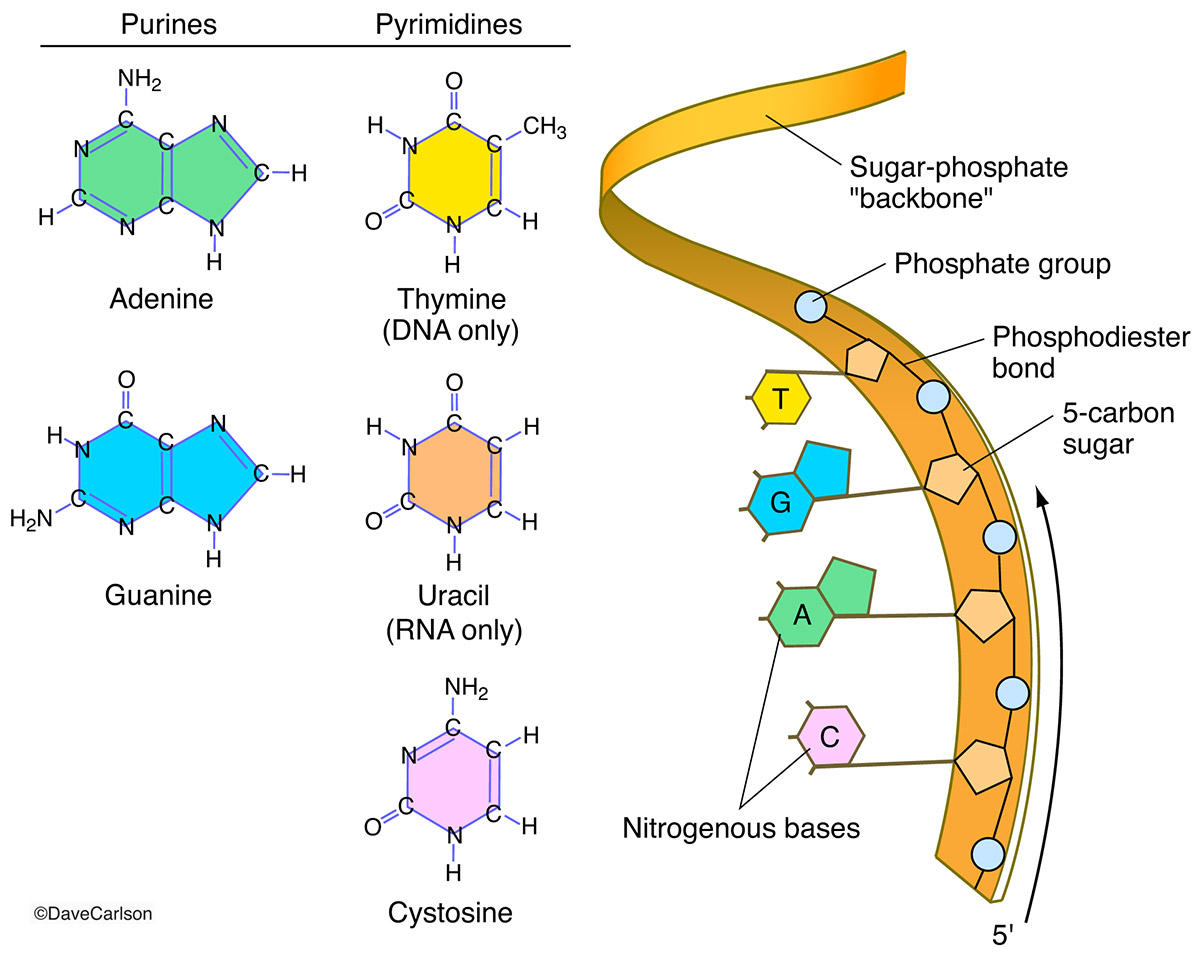
Nucleic Acid Structure Carlson Stock Art

19.2 Nucleic Acid Structure The Basics of General, Organic, and
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Nucleic acid
Nucleic Acid Structure

Nucleic acid definition, nucleic acid structure, function & types
Nucleotides Castell Alun High School Biology
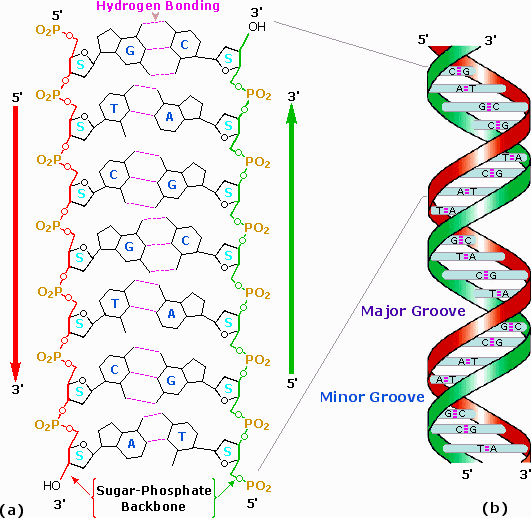
Nucleic Acids Chemistry LibreTexts
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dna-structure-518656657-570bc8895f9b5814082d6e34.jpg)
Nucleic Acids Structure and Function
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/nucleotide_base-5b6335bdc9e77c002570743e.jpg)
Nucleic Acids Function, Examples, and Monomers
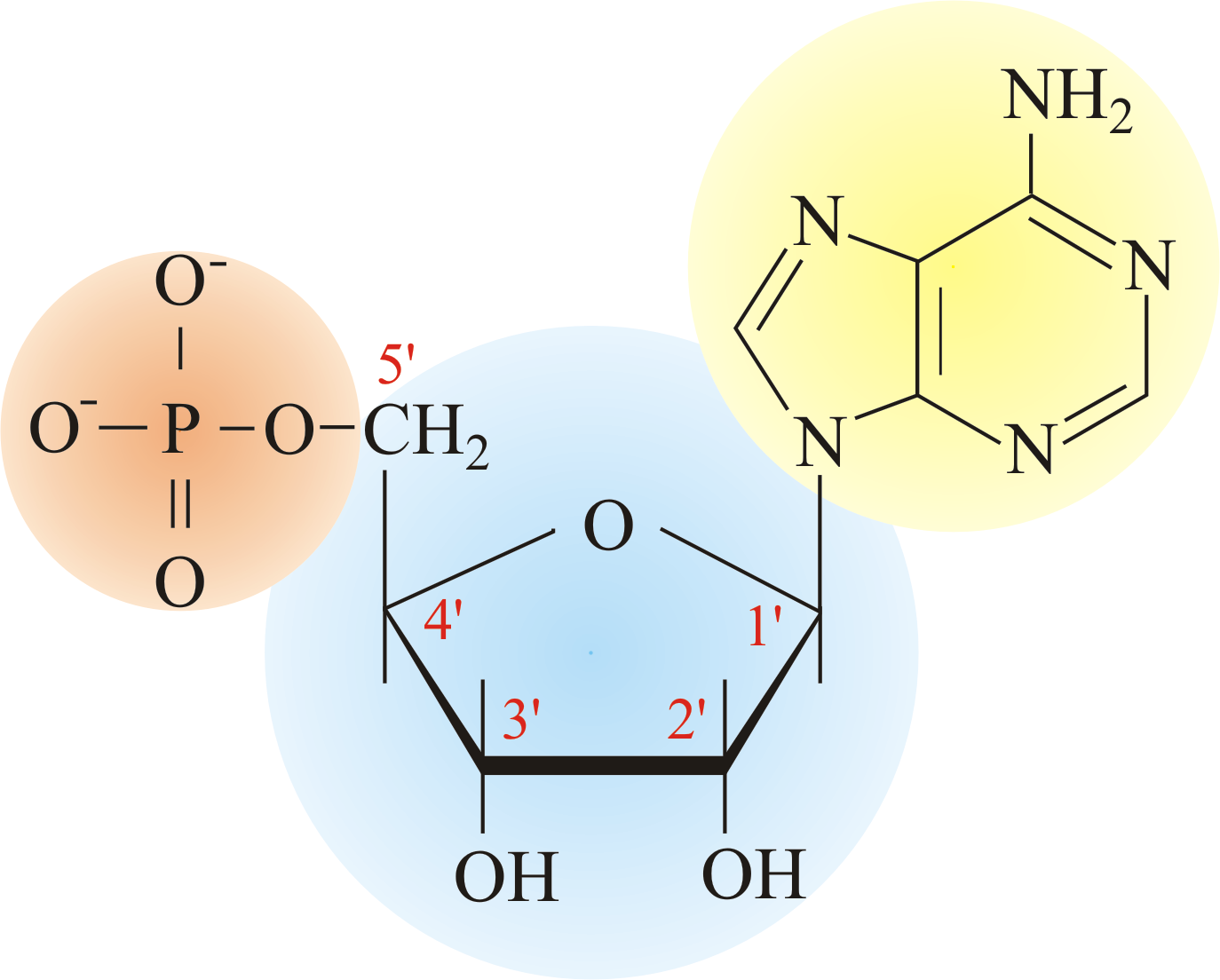
Nucleic Acids Jack's AP Biology Journal
The Two Main Types Of Nucleic Acids Are Deoxyribonucleic Acid (Dna) And Ribonucleic Acid (Rna).
Web Like Proteins, Nucleic Acids Have A Primary Structure That Is Defined As The Sequence Of Their Nucleotides.
Web Describe How A New Copy Of Dna Is Synthesized.
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (Dna) Nucleosides Nucleotides.
Related Post: