Prometaphase Drawing
Prometaphase Drawing - Mitosis, a key part of the cell cycle, involves a series of stages (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase) that facilitate cell division and genetic information transmission. The nuclear membrane dissolves, marking the beginning of prometaphase. Web prometaphase is the phase of mitosis following prophase and preceding metaphase in eukaryotic somatic cells. Web prometaphase is the second phase of mitosis, the process that separates the duplicated genetic material carried in the nucleus of a parent cell into two identical daughter cells. During prophase, the cell’s chromosomes have condensed and the cell’s centrosome, or microtubule organizing center, has divided and moved to opposite sides of the cell. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Define the quiescent g 0 phase. The stage in mitotic or meiotic nuclear division, following prophase and preceding metaphase, during which the condensed chromosomes become sequentially attached at their kinetochores to the spindle microtubules. In prometaphase the nuclear envelope breaks down (in many but not all eukaryotes) and the chromosomes attach to the mitotic spindle. Each phase involves characteristic steps in the process of chromosome. Proteins attach to the centromeres creating the kinetochores. Web prometaphase begins when the nuclear envelope disassembles, exposing nuclear structures and its contents to the cytoplasm. If a nucleolus is still present or you can distinguish a forming spindle, label these as well. You can learn more about these stages in the video on mitosis. The nuclear envelope is composed of. You may find that some accounts of mitosis further subdivide the process to include prometaphase between prophase and metaphase. Microtubules attach at the kinetochores and the chromosomes begin moving. During prophase, the cell’s chromosomes have condensed and the cell’s centrosome, or microtubule organizing center, has divided and moved to opposite sides of the cell. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Centrosomes. Kinetochores appear at the centromeres. Label the cell wall, plasma membrane, nuclear envelope (or where it would be), and chromosomes. The nuclear envelope is composed of two membrane barriers, the inner nuclear membrane (inm). Edupic graphical resource is a teacher designed free image resource for use by teachers and students. Describe the three stages of interphase. Web draw an onion cell in prophase. Web prometaphase is the second stage of mitosis. Web g1 phase (first gap) s phase (synthesis of dna) g2 phase (second gap) mitosis. Web today, mitosis is understood to involve five phases, based on the physical state of the chromosomes and spindle. During prophase, the cell’s chromosomes have condensed and the cell’s centrosome,. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. The stage in mitotic or meiotic nuclear division, following prophase and preceding metaphase, during which the condensed chromosomes become sequentially attached at their kinetochores to the spindle microtubules. These phases are prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. You may find that some accounts of mitosis further subdivide the process to include prometaphase between prophase and. Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Edupic graphical resource is a teacher designed free image resource for use by teachers and students. College of the redwoods via asccc open educational resources initiative. Prometaphase is the stage of eukaryotic cell division that falls between prophase and metaphase. Centrosomes and microtubules play pivotal roles in orchestrating this complex process, ensuring the successful. In prometaphase, the nuclear membrane breaks apart into numerous membrane vesicles, and the chromosomes inside form protein structures called kinetochores. The first phase of mitosis within m phase is called prophase. Each phase involves characteristic steps in the process of chromosome. Web today, mitosis is understood to involve five phases, based on the physical state of the chromosomes and spindle.. Web mitosis is commonly divided into four major phases: During prophase, the cell’s chromosomes have condensed and the cell’s centrosome, or microtubule organizing center, has divided and moved to opposite sides of the cell. Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. Define the quiescent g 0 phase. Web mitosis consists of four basic phases: Web prometaphase is the second stage of mitosis. Kinetochores appear at the centromeres. Metaphase is the third step in mitosis. Define the quiescent g 0 phase. Prometaphase is the stage of eukaryotic cell division that falls between prophase and metaphase. The first phase of mitosis within m phase is called prophase. Describe the three stages of interphase. In prometaphase, the nuclear membrane breaks apart into numerous membrane vesicles, and the chromosomes inside form protein structures called kinetochores. Define the quiescent g 0 phase. The stage in mitotic or meiotic nuclear division, following prophase and preceding metaphase, during which the condensed. Label the cell wall, plasma membrane, nuclear envelope (or where it would be), and chromosomes. The nuclear envelope is composed of two membrane barriers, the inner nuclear membrane (inm). Prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. You may find that some accounts of mitosis further subdivide the process to include prometaphase between prophase and metaphase. Web prometaphase is often referred to as “late prophase.” (though it’s also sometimes called “early metaphase” or referred to as a distinct phase entirely!) regardless, some really important things occur during prometaphase that propel cell division along and that help explain what happens in metaphase. Web prometaphase begins when the nuclear envelope disassembles, exposing nuclear structures and its contents to the cytoplasm. Spindle fibers align the chromosomes along the middle of the cell nucleus. Prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. In prometaphase, the nuclear membrane breaks apart into numerous membrane vesicles, and the chromosomes inside form protein structures called kinetochores. Web today, mitosis is understood to involve five phases, based on the physical state of the chromosomes and spindle. Proteins attach to the centromeres creating the kinetochores. Web draw an onion cell in prophase. Web g1 phase (first gap) s phase (synthesis of dna) g2 phase (second gap) mitosis. Microtubules attach at the kinetochores and the chromosomes begin moving. College of the redwoods via asccc open educational resources initiative. Centrosomes move toward opposite poles.
Ilustração Vetorial Da Fase De Mitose. Prometafase Ilustração do Vetor

Prometaphase Diagram

The Cell Cycle — The Biology Primer

Prométaphase — Wikipédia

prometafase de la división celular 6998569 Vector en Vecteezy

Prometaphase Diagram
![]()
BioRender Meiosis (03. Prometaphase I)

The Steps of Mitosis Biology for Majors I
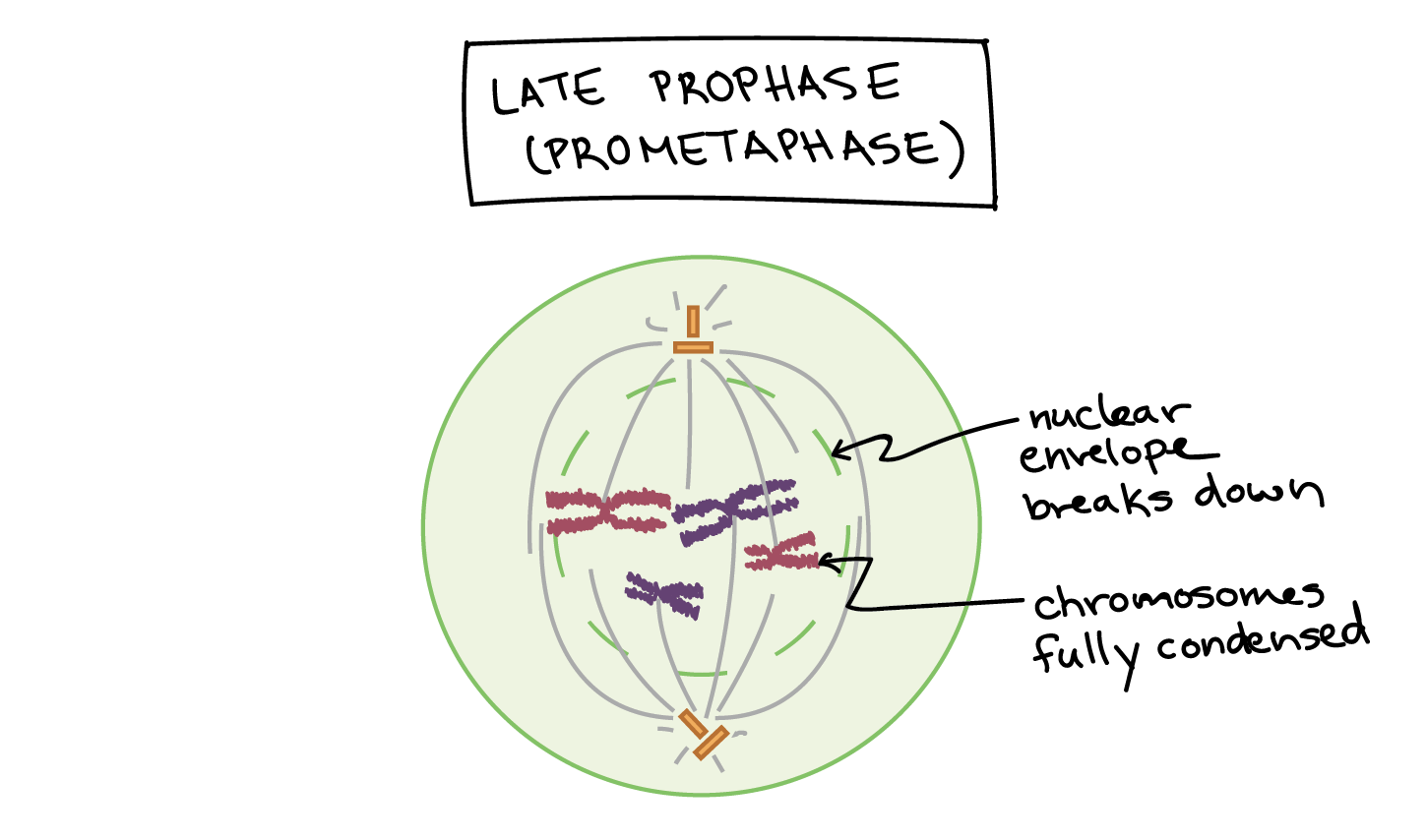
Prometaphase Diagram Wiring Diagram Pictures
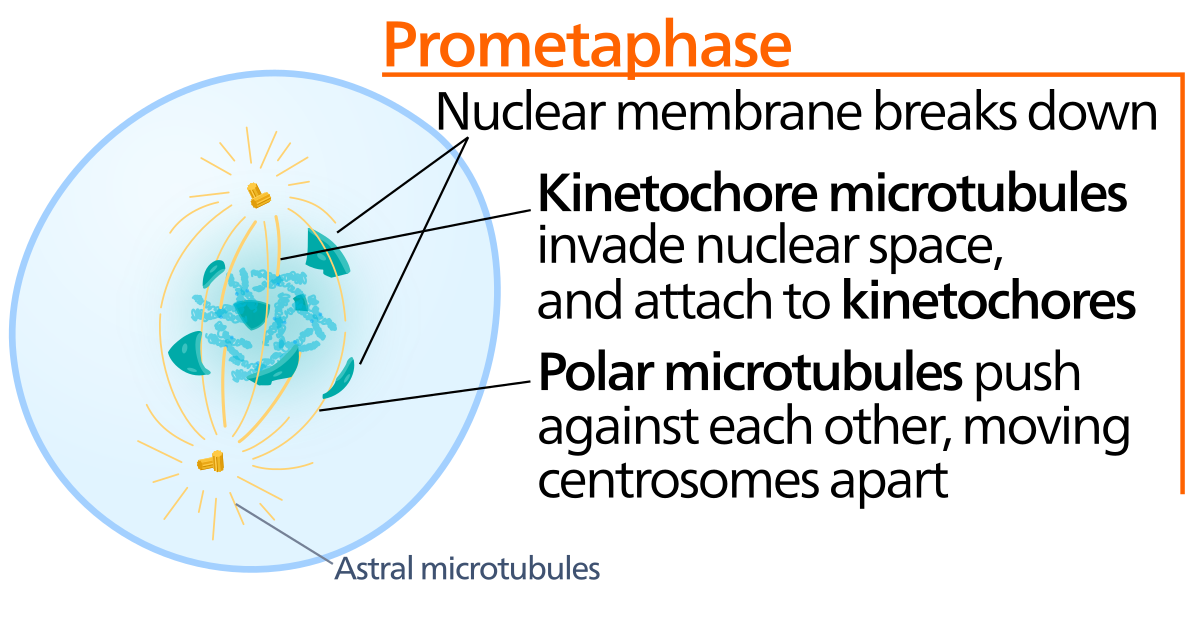
Prometaphase Wikipedia
Web Prometaphase Is The Second Stage Of Mitosis.
Kinetochores Appear At The Centromeres.
Web Prometaphase | Biology | Britannica.
During Prophase, The Cell’s Chromosomes Have Condensed And The Cell’s Centrosome, Or Microtubule Organizing Center, Has Divided And Moved To Opposite Sides Of The Cell.
Related Post: