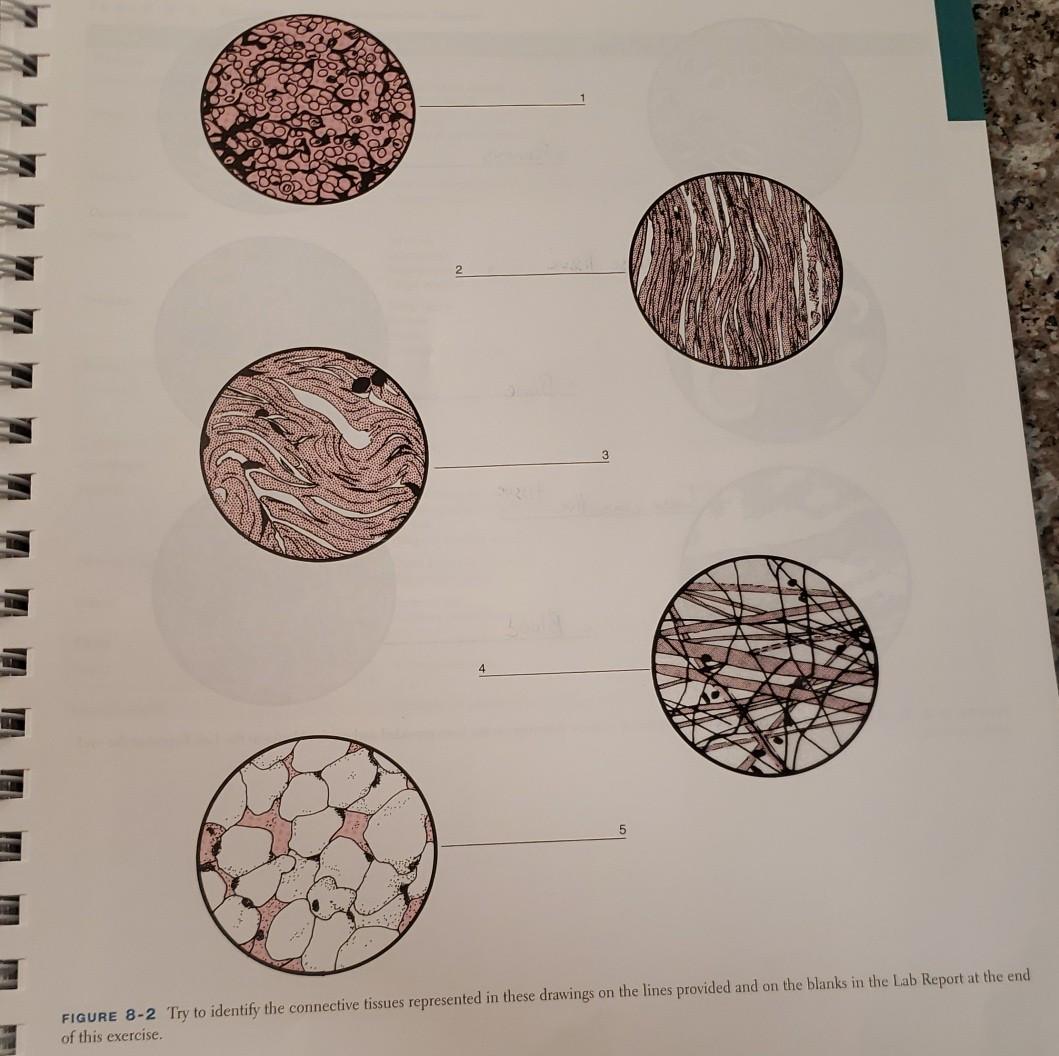
Reticular Connective Tissue Drawing
Reticular Connective Tissue Drawing - Web reticular connective tissue is composed of a meshwork of reticular fibers (type iii collagen) in an open arrangement. Watch the video tutorial now. Web reticular tissue is a type of connective tissue proper with an extracellular matrix consisting of an interwoven network of reticular fibers that provide a strong yet somewhat flexible framework (known as the stroma) for other types of functional cells to. They are not visible with hematoxylin & eosin (h&e), but are specifically stained by silver. Location of reticular connective tissue. Comprises an abundance of reticular fibers that form complicated branching and interweaving patterns. Found in lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow. Learn everything about it in the f. Web reticular tissue is a special subtype of connective tissue that is indistinguishable during routine histological staining. Web o correlate the histological compositions and organizations of ct proper, reticular ct, and adipose ct and their locations and functions. These fibers are actually type iii collagen fibrils. Forms stroma of liver, spleen, bone marrow, and lymph nodes. Reticular fibers are composed of thin and delicately woven strands of type iii collagen. These fibers form a supportive structure in various organs such as the bone marrow, liver, and lymphoid organs, which include the spleen, lymph nodes, and tonsils. The cells. Web reticular tissue is a type of connective tissue proper with an extracellular matrix consisting of an interwoven network of reticular fibers that provide a strong yet somewhat flexible framework (known as the stroma) for other types of functional cells to. Connective tissue function and composition. Web reticular connective tissue is a type of connective tissue with a network of. Comprises an abundance of reticular fibers that form complicated branching and interweaving patterns. Reticular connective tissue is named for the reticular fibers which are the main structural part of the tissue. Fine reticular fibers stain faintly; Web reticular tissue is a special subtype of connective tissue that is indistinguishable during routine histological staining. Web reticular connective tissue 10x. This tissue must be specifically stained and is usually taken from a lymph node or the spleen. Reticular fibers are not unique to reticular connective tissue, but only in this tissue type are they dominant. Web form a tightly woven fabric that joins connective tissue to adjacent tissues. Web reticular connective tissue 10x. Web reticular tissue is a special type. These fibers are actually type iii collagen fibrils. Is a fine interlacing network of reticular fibers and reticular cells. Web form a tightly woven fabric that joins connective tissue to adjacent tissues. Appearance and features of the reticular connective tissue. Web o correlate the histological compositions and organizations of ct proper, reticular ct, and adipose ct and their locations and. Reticular connective tissue is named for the reticular fibers which are the main structural part of the tissue. Is a fine interlacing network of reticular fibers and reticular cells. Reticular tissue, a type of loose connective tissue in which reticular fibers are the most prominent fibrous component, forms the supporting framework of the lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils), bone. These fibers form a supportive structure in various organs such as the bone marrow, liver, and lymphoid organs, which include the spleen, lymph nodes, and tonsils. This special connective tissue forms the stroma for hemopoietic tissues and lymphoid structures and organs, except the thymus. Reticular connective tissue is named for the reticular fibers which are the main structural part of. If there is abundant space between protein fibers, the tissue is likely one of the loose connective tissues. Forms stroma of liver, spleen, bone marrow, and lymph nodes. These fibers form a supportive structure in various organs such as the bone marrow, liver, and lymphoid organs, which include the spleen, lymph nodes, and tonsils. The cells that make the reticular. Location of reticular connective tissue. The cells that make the reticular fibers are fibroblasts called reticular cells. Web form a tightly woven fabric that joins connective tissue to adjacent tissues. This scaffolding supports other cell types including white blood cells, mast cells, and macrophages. Reticular tissue, a type of loose connective tissue in which reticular fibers are the most prominent. This special connective tissue forms the stroma for hemopoietic tissues and lymphoid structures and organs, except the thymus. Comprises an abundance of reticular fibers that form complicated branching and interweaving patterns. Identify the different cells and fiber types found in connective tissue. Connective tissue is subdivided into the following categories and. The cells that make the reticular fibers are fibroblasts. Web reticular connective tissue 10x. May anchor to collagenous septa, which divide organs into lobes. Forms stroma of liver, spleen, bone marrow, and lymph nodes. Watch the video tutorial now. Learn everything about it in the f. Web reticular connective tissue is composed of a meshwork of reticular fibers (type iii collagen) in an open arrangement. Reticular cells are specialized fibroblasts that synthesize and hold the fibers. Web reticular connective tissue forms an internal scaffolding for certain organs, such as lymph nodes, bone marrow, and the spleen. Reticular tissue, a type of loose connective tissue in which reticular fibers are the most prominent fibrous component, forms the supporting framework of the lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, spleen, tonsils), bone marrow and liver. Comprises an abundance of reticular fibers that form complicated branching and interweaving patterns. Reticular tissue, a form of loose connective tissue wherein reticular fibres are the most predominant fibrous constituent, serves as the supporting structure of the bone marrow, liver and lymphoid organs (spleen, lymph nodes, and tonsils). Reticular fibers are not unique to reticular connective tissue, but only in this tissue type are they dominant. Web reticular connective tissue 40x. Web reticular tissue is a type of connective tissue proper with an extracellular matrix consisting of an interwoven network of reticular fibers that provide a strong yet somewhat flexible framework (known as the stroma) for other types of functional cells to. Appearance and features of the reticular connective tissue. Reticular fibers are abundant in lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, spleen), bone marrow and liver.
Connective Tissue Supports and Protects · Anatomy and Physiology
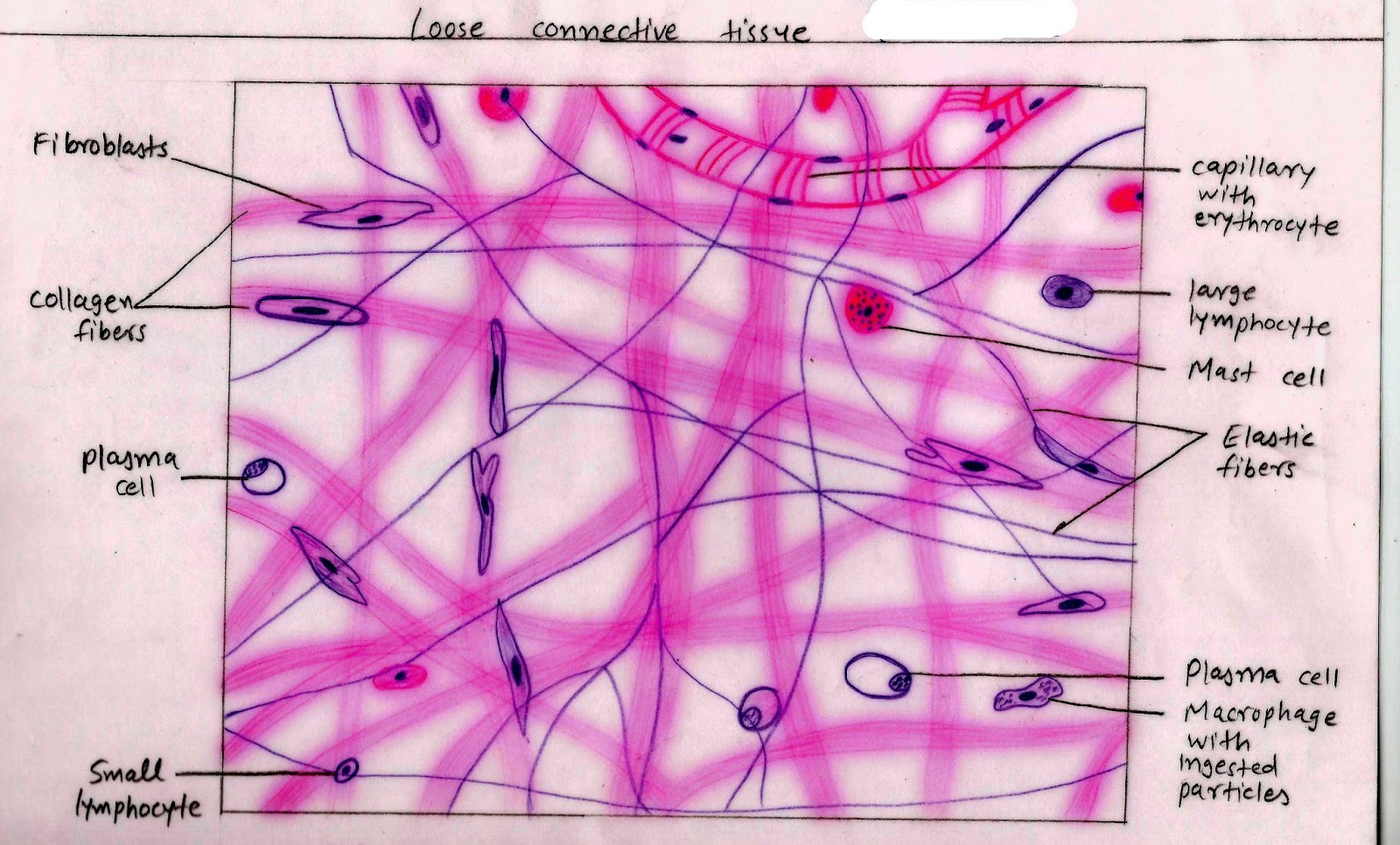
Histology Image Connective tissue
Reticular Connective Tissue Drawing Master the Art of Illustrating
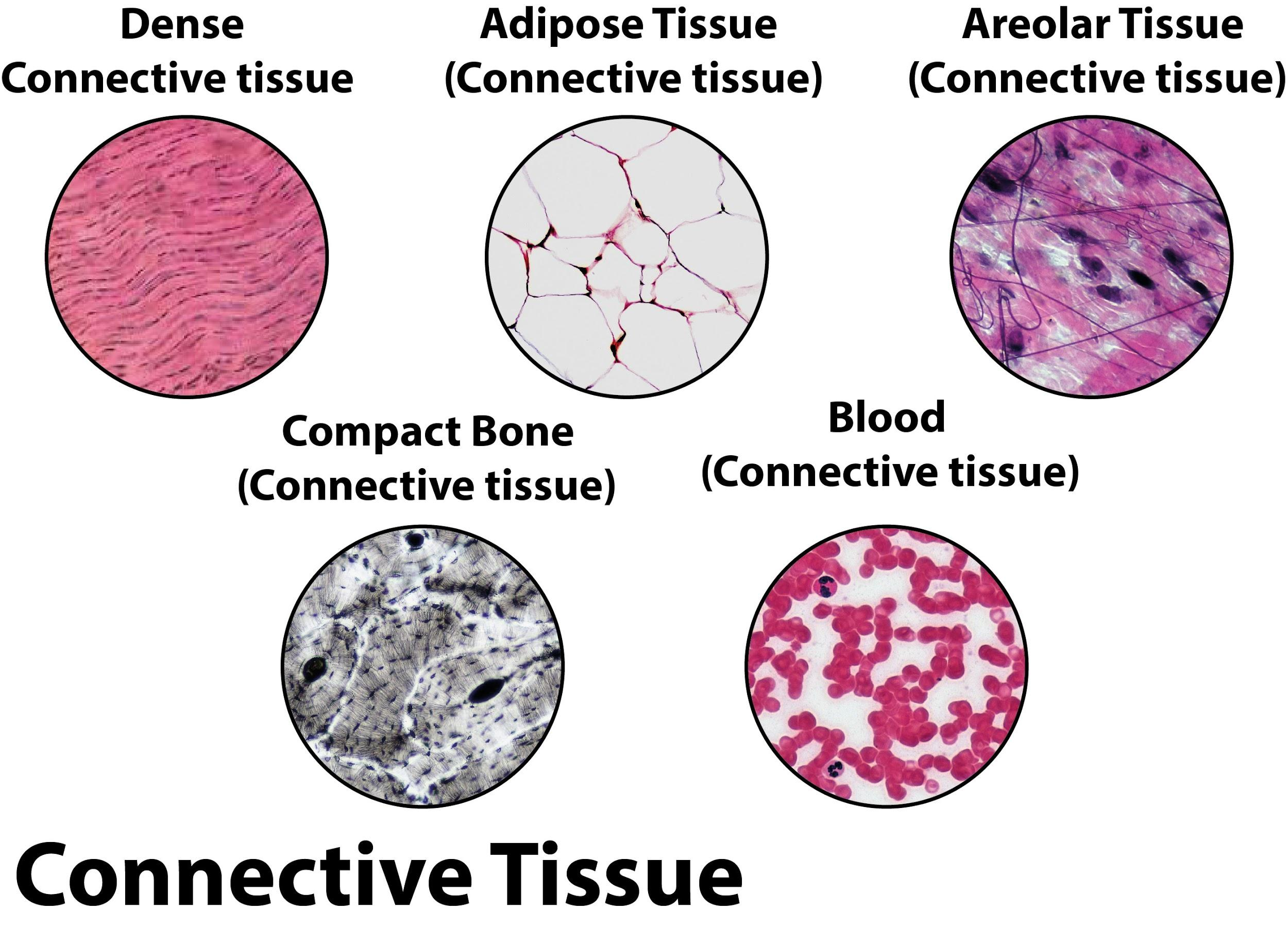
Give the characteristics of connective tissue.
Reticular Connective Tissue 20x Histology

Mammalian Tissues Lab Notebook Students Coursework

Reticular Connective Tissue Structure

Connective Tissue Reticular cross section magnification… Flickr

Reticular Connective Tissue Labeled

Reticular Connective Tissue, 40X Histology
They Are Not Visible With Hematoxylin & Eosin (H&E), But Are Specifically Stained By Silver.
These Tissues Have A Peculiar Feature;
Reticular Fibers Are Composed Of Thin And Delicately Woven Strands Of Type Iii Collagen.
Web O Correlate The Histological Compositions And Organizations Of Ct Proper, Reticular Ct, And Adipose Ct And Their Locations And Functions.
Related Post: