Skeletal Muscle Tissue Drawing
Skeletal Muscle Tissue Drawing - As you go through these slides, refer to this schematic drawing showing the key structural features and relative sizes of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle as you would observe them with the highest objective setting. There are three layers of connective tissue: The ability to create and share still and moving images such as drawing, graphic illustrations, photographic reproduction and videos is one of the most important technological advancements of this age. Web skeletal muscles contain connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves. Thus, it is divided into three basic types: Skeletal muscle is a specialized contractile tissue found in animals which functions to move an organism’s body. Relate muscle fiber structure to the functional units of muscles. Web skeletal muscles contain connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves. Each skeletal muscle fiber comprises compactly packed long myofibrils that arrange parallel to the long axis. Describe the organization of a sarcomere. The skeletal muscle under a microscope shows long, cylindrical, unbranched fibers and flat nuclei. Web draw the complete human skeletal system. It is classified as a striated muscle tissue, which functions to contract and permit movements under voluntary control. There are three layers of connective tissue: Web each skeletal muscle has three layers of connective tissue (called “mysia”) that enclose. Skeletal muscles vary considerably in size, shape, and arrangement of fibers. Thus, it is divided into three basic types: Describe the organization of a sarcomere. Correlate the microscopic organization of a muscle fiber with the mechanism of contraction and relaxation. Web original author (s): Correlate the microscopic organization of a muscle fiber with the mechanism of contraction and relaxation. Describe the histological organization of skeletal muscle. Web anatomy of a skeletal muscle cell (video) | khan academy. Under the light microscope, muscle cells appear striated with many nuclei squeezed along the membranes. By the end of this section, you will be able to: Web original author (s): Under the light microscope, muscle cells appear striated with many nuclei squeezed along the membranes. By the end of this section, you will be able to: It is classified as a striated muscle tissue, which functions to contract and permit movements under voluntary control. Blood vessels and nerves enter the connective tissue and branch. There are three layers of connective tissue: Describe the histological organization of skeletal muscle. Explain how muscles work with tendons to move the body. Blood vessels and nerves enter the connective tissue and branch in the cell. This longitudinal section allows the morphology of individual skeletal muscle cells (or fibers) to be examined. Web in this video i have shown the simplest way of drawing muscle drawing. Skeletal muscle is one of the three types of muscle tissue, alongside cardiac and smooth muscle. Web the term temporomandibular disorders (tmd) is broad and refers to various musculoskeletal and neuromuscular disorders that affect the temporomandibular joint, the masticatory muscles and associated tissues [1, 2].tmd is. Identify areas of the skeletal muscle. By the end of this section, you will be able to: It is the pen diagram of skeletal, smooth and cardiac muscle for class 10, 11 and 12. Skeletal muscle is a specialized contractile tissue found in animals which functions to move an organism’s body. Web skeletal muscle is an excitable, contractile tissue responsible. The skeletal muscle fibres are multinucleated. Web in this video i have shown the simplest way of drawing muscle drawing. Identify areas of the skeletal muscle. Why do many skeletal muscles work in pairs? Describe the histological organization of skeletal muscle. Skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle (figure 10.1.1). Compare motor and sensory innervation of skeletal muscle tissue. Striated skeletal muscle, textus muscularis striatus skeletalis. Describe the organization of a sarcomere. Why is skeletal muscle tissue striated? Relate muscle fiber structure to the functional units of muscles. These muscle cells are slender and long and are termed as muscle fibres. Web anatomy of a skeletal muscle cell (video) | khan academy. It is classified as a striated muscle tissue, which functions to contract and permit movements under voluntary control. It is the pen diagram of skeletal, smooth. Blood vessels and nerves enter the connective tissue and branch. Identify areas of the skeletal muscle. Web each skeletal muscle has three layers of connective tissue (called “mysia”) that enclose it and provide structure to the muscle as a whole, and also compartmentalize the muscle fibers within the muscle (figure \ (\pageindex {1}\) ). The skeletal muscle under a microscope shows long, cylindrical, unbranched fibers and flat nuclei. There are three layers of connective tissue: Web the term temporomandibular disorders (tmd) is broad and refers to various musculoskeletal and neuromuscular disorders that affect the temporomandibular joint, the masticatory muscles and associated tissues [1, 2].tmd is the second most common musculoskeletal disorder causing pain and disability [3, 4].treatment options for tmd. As you go through these slides, refer to this schematic drawing showing the key structural features and relative sizes of skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle as you would observe them with the highest objective setting. Within muscles, there are layers of connective tissue called the epimysium, perimysium, and endomysium. Web in this video i have shown the simplest way of drawing muscle drawing. Skeletal muscle is one of the three types of muscle tissue, alongside cardiac and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle fibers are organized into groups called fascicles. Web skeletal muscles contain connective tissue, blood vessels, and nerves. Thus, it is divided into three basic types: Identify areas of the skeletal muscle. Relate muscle fiber structure to the functional units of muscles. Muscle tissue is formed by elongated and contractile cells with specific morphofunctional characteristics.
(A) Illustration of skeletal muscle structure copied with permission

How To Draw Structure Of Skeletal Muscle YouTube

Skeletal Muscle Tissue Diagram Quizlet
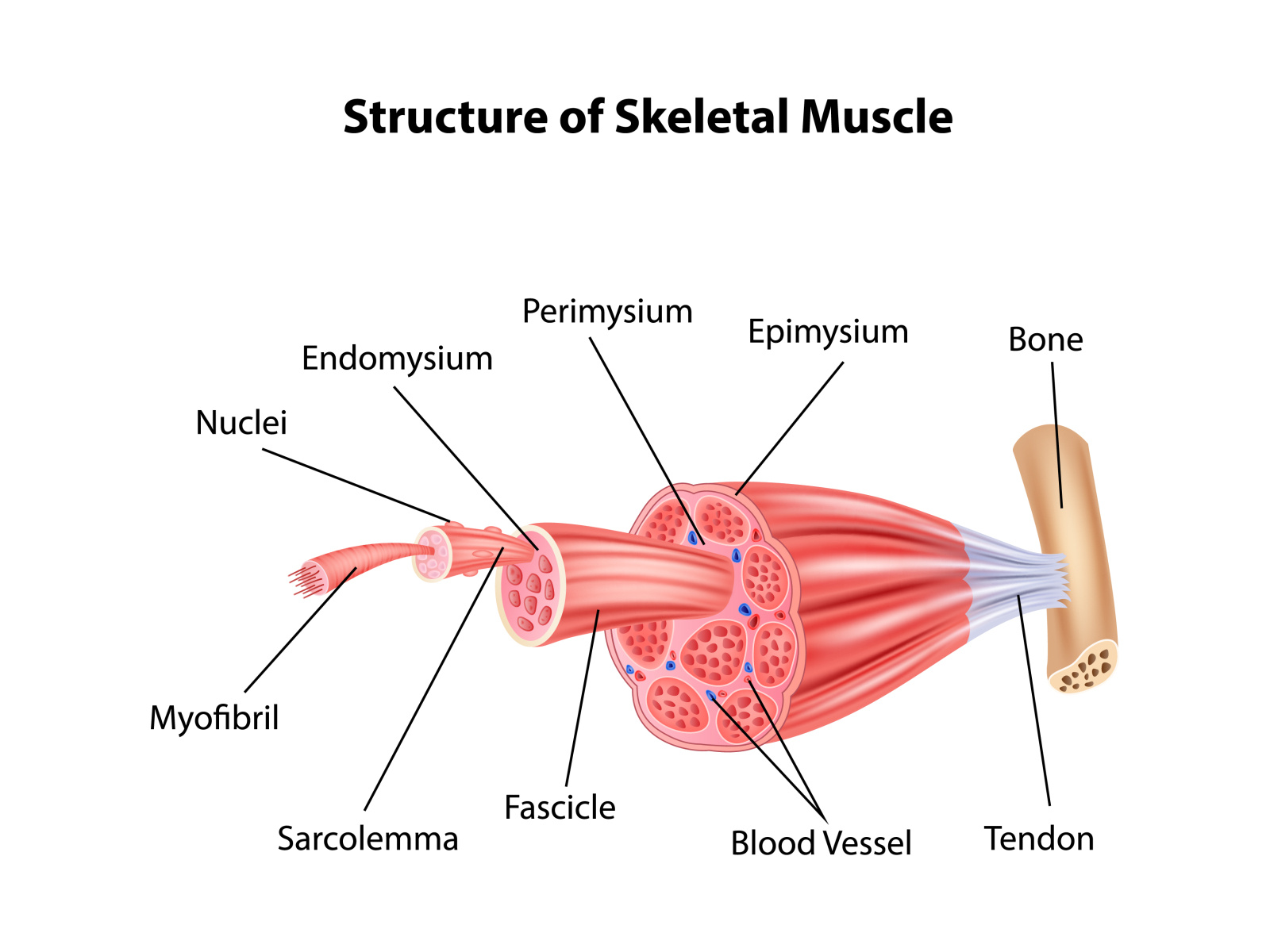
Structure Skeletal Muscle Anatomy by Tigatelu on Dribbble

Skeletal muscle tissue. Skeletal muscle consists of muscle fibers that

How to draw " Skeletal ( voluntary Muscles )" step by step in a easy
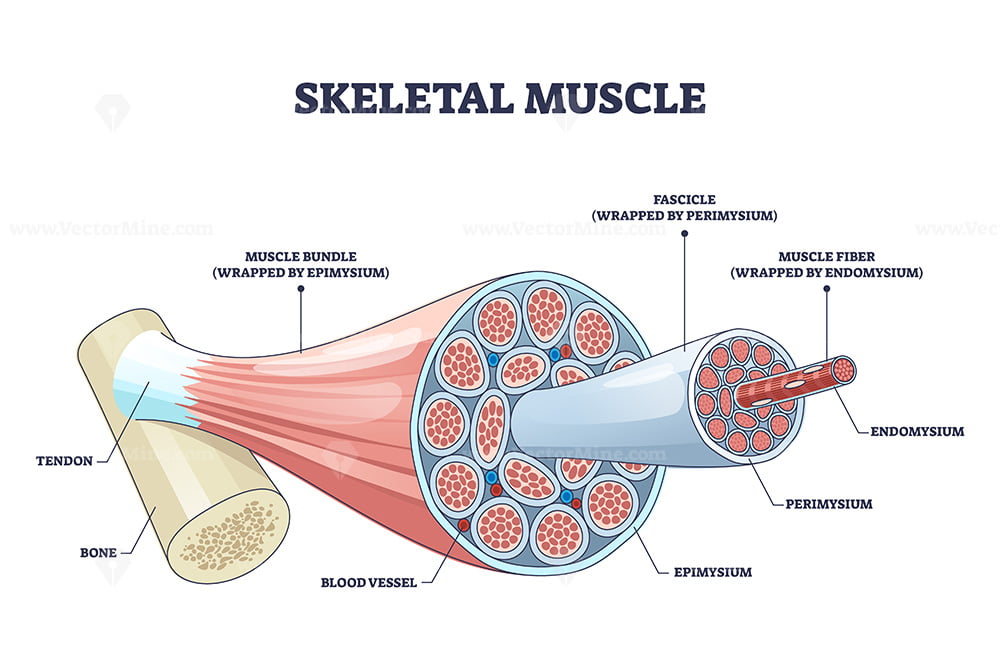
Skeletal muscle structure with anatomical inner layers outline diagram

Anatomy Of Muscle Cell The Anatomy Stories

Muscle Tissue Drawing at GetDrawings Free download
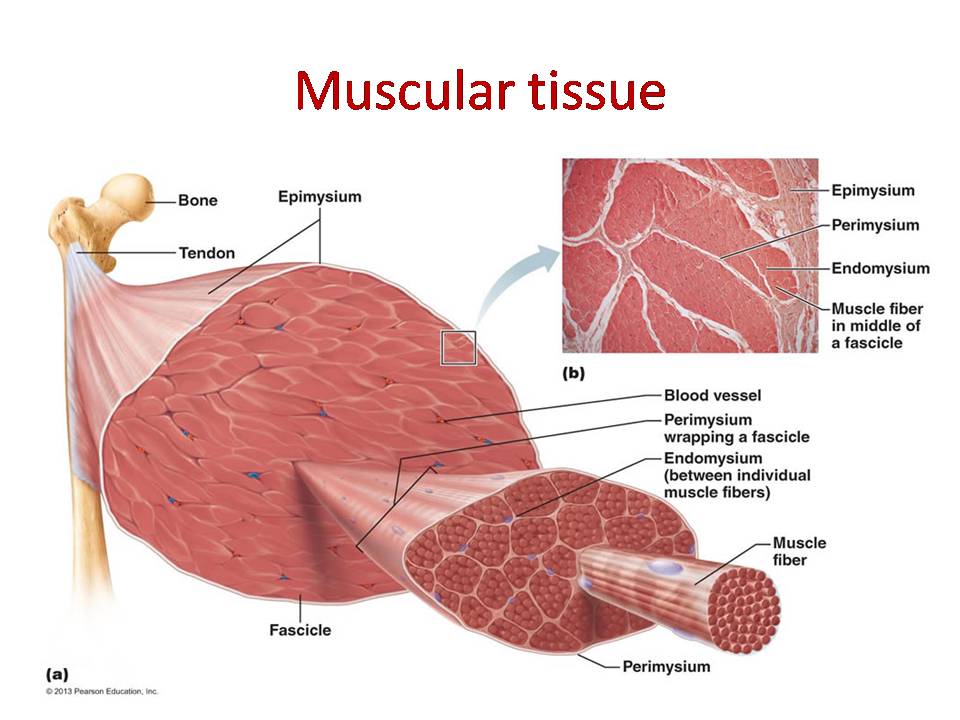
Muscle Tissue Diagram Labeled
It Attaches To Bones And The Orbits Through Tendons.
There Are Three Layers Of Connective Tissue:
Web Anatomy Of A Skeletal Muscle Cell (Video) | Khan Academy.
It Is Classified As A Striated Muscle Tissue, Which Functions To Contract And Permit Movements Under Voluntary Control.
Related Post: