Vasovagal Reaction To Blood Draw
Vasovagal Reaction To Blood Draw - Web commonly referred to as vasovagal syncope or a vasovagal response, essentially what happens is the patient’s blood pressure suddenly drops and not enough oxygen can reach the brain. A simple maneuver to prevent or diminish vasovagal reactions would be beneficial. It's rare for it to occur if you’re lying down. It could be anxiety, distress, or sometimes even the sight of blood is enough to trigger it. Giving blood, getting vaccinated, or standing on a stuffy, crowded train can result in dizziness and a loss of consciousness for some people. However, the mechanism behind needle fear and the vvr response are not yet well understood. Diehl, ) suggests that vvr developed from the adaptive process of hemorrhagic fainting, perhaps as a means of preparing for anticipated blood loss. We present a systematic review of interventions designed to prevent or reduce vvrs in blood donors. It may also be called neurocardiogenic syncope. There’s not a single cause for this reaction; Web commonly referred to as vasovagal syncope or a vasovagal response, essentially what happens is the patient’s blood pressure suddenly drops and not enough oxygen can reach the brain. These patients experienced a very common reaction known as vasovagal syncope. It's usually not harmful and not a sign of a more serious problem. During the physical exam, your doctor will. A simple maneuver to prevent or diminish vasovagal reactions would be beneficial. The vasovagal syncope trigger causes your heart rate and blood pressure to drop suddenly. A couple of my patients have passed out while having their blood drawn. Web bymuratdeniz / getty images. Web vasovagal syncope occurs when your body reacts so strongly to a trigger—like having blood drawn. Web vasovagal reactions (vvrs) are encountered in blood donors at blood centers, manifesting with symptoms such as pallor, perspiration, dizziness, nausea, and fainting 1. Web vasovagal reactions in blood donors: Web people with needle fear experience not only anxiety and stress but also vasovagal reactions (vvr), including nausea, dizziness, sweating, pallor changes, or even fainting. This causes your heart to. Both fear and draw time were significant predictors of vasovagal reactions, with observed reaction rates of 31.2% for fearful donors whose blood draw lasted 10 minutes or more versus 5.0% for nonfearful donors whose draw lasted less than 6 minutes. Web bymuratdeniz / getty images. This narrative review examines current research on risk factors, prevention methods and management strategies for. A simple maneuver to prevent or diminish vasovagal reactions would be beneficial. Web what causes a vasovagal response during a blood draw? Reflex syncope describes any form of syncopal episode caused by a failure in the autoregulation of blood pressure, and ultimately, a drop in cerebral perfusion pressure resulting in a transient loss of consciousness. It's the most common cause. It could be anxiety, distress, or sometimes even the sight of blood is enough to trigger it. Giving blood, getting vaccinated, or standing on a stuffy, crowded train can result in dizziness and a loss of consciousness for some people. A couple of my patients have passed out while having their blood drawn. These patients experienced a very common reaction. However, the mechanism behind needle fear and the vvr response are not yet well understood. Vasovagal reactions in blood donors: A brief period right before vasovagal syncope may happen where you’re most likely to have symptoms. 2 transcranial doppler (tcd) is used to evaluate cerebral blood flow and to differentiate the types of syncope. Web vasovagal reactions (vvrs) in blood. Web vasovagal reactions in blood donors: It could be anxiety, distress, or sometimes even the sight of blood is enough to trigger it. Web most of the time, vasovagal syncope happens when you’re standing or sitting. The vasovagal syncope trigger causes your heart rate and blood pressure to drop suddenly. He or she may also massage the main arteries in. Both fear and draw time were significant predictors of vasovagal reactions, with observed reaction rates of 31.2% for fearful donors whose blood draw lasted 10 minutes or more versus 5.0% for nonfearful donors whose draw lasted less than 6 minutes. Vasovagal reactions in blood donors: Giving blood, getting vaccinated, or standing on a stuffy, crowded train can result in dizziness. A brief period right before vasovagal syncope may happen where you’re most likely to have symptoms. It's usually not harmful and not a sign of a more serious problem. Web vasovagal reactions (vvrs) in blood donors have significant implications for the welfare of donors, donor retention and the management of donor sessions. An episode of fainting from vasovagal syncope usually. It's usually not harmful and not a sign of a more serious problem. A vasovagal response happens when your nervous system reacts to a trigger — like stress or pain — and causes your blood pressure to drop. Web vasovagal reactions (vvrs) are encountered in blood donors at blood centers, manifesting with symptoms such as pallor, perspiration, dizziness, nausea, and fainting 1. It may also be called neurocardiogenic syncope. During the physical exam, your doctor will listen to your heart and take your blood pressure. Web vasovagal syncope occurs when your body reacts so strongly to a trigger—like having blood drawn or being scared—that your heart rate and blood pressure plummet and you faint. Web vasovagal reactions to blood donation though generally mild and account for about 1% of donations, causes embarrassment/injury to the donors, lower likely return rates for future donations etc. Vasovagal reactions in blood donors: When the vagus nerve is overstimulated, the body's blood vessels dilate, especially those in the lower extremities, and the heart temporarily slows down. It's rare for it to occur if you’re lying down. Electronic databases were searched for eligible randomised trials to march 2015. 2 transcranial doppler (tcd) is used to evaluate cerebral blood flow and to differentiate the types of syncope. Web vasovagal syncope is a condition that leads to fainting in some people. Web people with needle fear experience not only anxiety and stress but also vasovagal reactions (vvr), including nausea, dizziness, sweating, pallor changes, or even fainting. It could be anxiety, distress, or sometimes even the sight of blood is enough to trigger it. 2 although a great deal of effort has been applied to the preve.:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vasovagal-reflex-1945072-5c3b87a44cedfd0001622493.png)
Vagal Response Causes and Triggers
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/vasovagal-cardioneurogenic-syncope-1746389-color3-ce8587834a804fb994d99352d0d7329b.jpg)
Vasovagal (Neurocardiogenic) Syncope Causes and Treatment

Vasovagal reaction? Student Doctor Network

Vasovagal Syncope What Is It, Causes, Prevention, and More Osmosis
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/ibs-and-the-vasovagal-reflex-1945272-v3-5c1abff946e0fb0001c6a121.png)
Überblick über den Vasovagalreflex

having vasovagal syncope after getting my blood drawn YouTube

Vasovagal Syncope What Is It, Causes, Prevention, and More Osmosis

Vasovagal Syncope explained using a 3D medical animation still shot
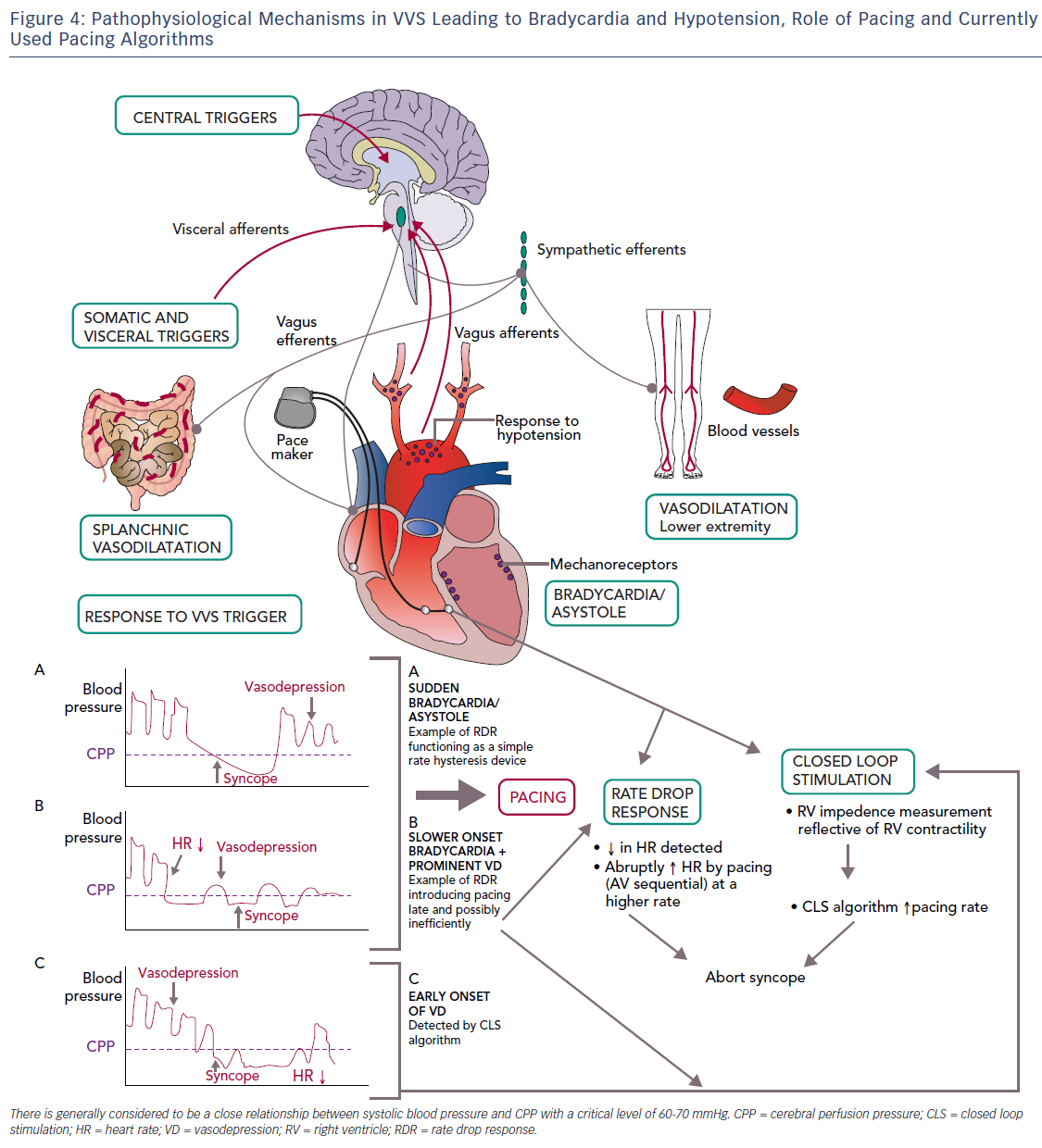
Figure 4 Pathophysiological Mechanisms in VVS Leading to Bradycardia
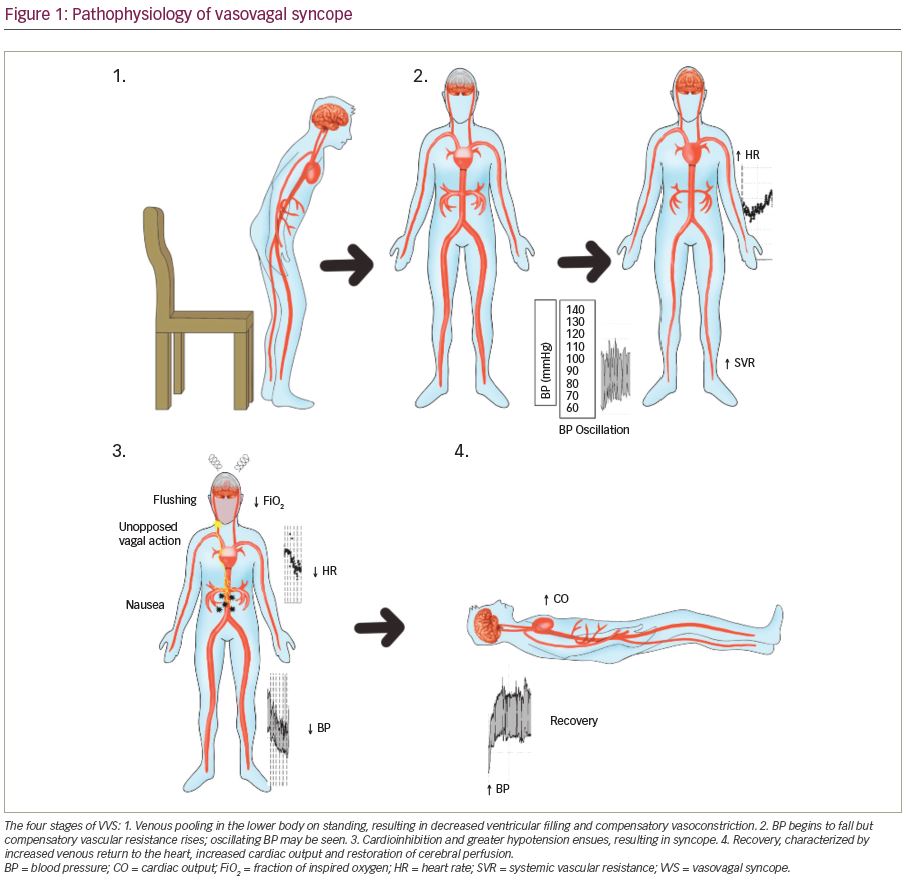
Vasovagal Syncope A Review of Current and Future Strategies touchCARDIO
Both Fear And Draw Time Were Significant Predictors Of Vasovagal Reactions, With Observed Reaction Rates Of 31.2% For Fearful Donors Whose Blood Draw Lasted 10 Minutes Or More Versus 5.0% For Nonfearful Donors Whose Draw Lasted Less Than 6 Minutes.
Let’s Explain How That Happens.
There’s Not A Single Cause For This Reaction;
A Couple Of My Patients Have Passed Out While Having Their Blood Drawn.
Related Post: